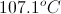All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Solubility Rules
All of the following compounds are soluble in water except __________.
Compounds that contain sulfate groups ( 

Compounds that contain nitrates (

Example Question #31 : Solution Chemistry
Which salt will produce a basic solution when dissolved in water?
When 


Each of the other answer options will result in at least one acidic compound when dissolved in solution.
Example Question #701 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Substances for which pure water would not be an efficient solvent are __________.
those that tend to form hydrogen bonds
those with evenly dispersed electrons
those that have large dipole moments
those that have high charge densities
those with evenly dispersed electrons
Since water is polar, it dissolves substances that have electrostatic charge due to electron arrangement. All of the answer choices describe molecules that would have positive and negative components except those with evenly dispersed electrons. This describes a nonpolar molecule, which would not dissolve in water.
Example Question #1 : Colligative Properties
The values for normal boiling and freezing points, along with 

A 
Magnesium phosphide in benzene
Sodium chloride in acetic acid
Magnesium phosphide in acetic acid
Sodium chloride in benzene
Magnesium phosphide in acetic acid
Boiling point elevation depends on three variables: the boiling point elevation constant of the solvent, the van't Hoff factor of the solute, and the molality of the solution. In this question, molality is held constant.
First, calculate the van't Hoff for each compound.
Ultimately, we are looking for the greatest product of the boiling point elevation constant and van't Hoff factor (since molality is constant).
Magnesium phosphide has the greater van't Hoff factor and acetic acid has the greater boiling point elevation constant. A solution of magnesium phosphide in acetic acid will thus have the greatest boiling point elevation.
Example Question #1 : Boiling Point
The values for normal boiling and freezing points, along with 




We first need to find the boiling point elevation with the equation:
Ammonium phosphate has an van't Hoff value of four; each molecule dissociates into four ions in solution. To calculate the molality, we need to find moles of solute per kilogram of solution.
Next, use the molality, van't Hoff factor, and boiling point elevation constant to solve for the increase in boiling point.
Add this increase to the boiling point of pure water to find the boiling point of the solution.
Example Question #1 : Boiling Point
Boiling point is the temperature a liquid needs to achieve in order to begin its transformation into a gaseous state. Campers and hikers who prepare food during their trips have to account for differences in atmospheric pressure as they ascend in elevation. During the ascent, the decrease in atmospheric pressure changes the temperature at which water boils.
Further complicating the matter is the observation that addition of a solute to a pure liquid also changes the boiling point. Raoult’s Law can be used to understand the changes in boiling point if a non-volatile solute is present, as expressed here.
In this law, 


Two campers are preparing food at an altitude of 13,000 feet on a mountain in Colorado. Which of the following is true as they boil a pot of water?
They will likely have to cook their food longer than at sea level, since it takes more heat to make vapor pressure match atmospheric pressure
They will likely have to cook their food longer than at sea level, since it takes less heat to make vapor pressure match atmospheric pressure
They will likely have to cook their food a shorter time than at sea level, since it takes more heat to make vapor pressure match atmospheric pressure
They will likely have to cook their food a shorter time than at sea level, since it takes less heat to make vapor pressure match atmospheric pressure
If they add salt to the water, it will help speed the rate at which the water boils
They will likely have to cook their food longer than at sea level, since it takes less heat to make vapor pressure match atmospheric pressure
The local atmospheric pressure at 13,000 feet is less than the pressure at sea level; therefore, it takes less heat to make the vapor pressure meet the local atmospheric pressure. Heat added to the system easily exits again as the water is converted to steam, leaving less heat in the water to cook the food. Food cooks more slowly as a result.
Example Question #2 : Boiling Point
Boiling point is the temperature a liquid needs to achieve in order to begin its transformation into a gaseous state. Campers and hikers who prepare food during their trips have to account for differences in atmospheric pressure as they ascend in elevation. During the ascent, the decrease in atmospheric pressure changes the temperature at which water boils.
Further complicating the matter is the observation that addition of a solute to a pure liquid also changes the boiling point. Raoult’s Law can be used to understand the changes in boiling point if a non-volatile solute is present, as expressed here.
In this law, 


The change in boiling point with addition of a solute is a colligative property of a solution. Which of the following are also examples of colligative properties?
I. Vapor pressure reduction
II. Color emission with dissolution of a solute
III. Osmotic pressure
I and III, only
I, II, and III
III, only
I and II, only
II and III, only
I and III, only
Colligative properties are defined as properties that depend entirely upon the ratio of the number of solute particles to the number of solvent particles. Only osmotic pressure and vapor pressure depression are examples of such phenomena. While color emission is a property of a solution, it depends on the chemical species involved, and not the number of particles.
Example Question #1 : Colligative Properties
Suppose two containers each contain the same amount of solvent. 2m NaCl solution is added to the first container, and a mystery solution is added to the second container. Upon heating the flasks, it is determined that the second container has a higher boiling point than the first container. Assume the solutions are ideal.
Based on the above information, which of the following compounds could have been added to container 2?
1m MgCl2
2m CaF2
1m NaCl
3m C6H12O6
2m CaF2
Based on the equation 

The sodium choride added to container 1 has a molality of 2, as well as a van't Hoff factor of 2. As a result, we are looking for a compound that has a larger combination of these two factors, which would cause a higher boiling point. 2m CaF2 has a molality of 2 and a van't Hoff factor of 3. Since this combination of factors in container 2 would be higher than the combination in container 1, we can conclude that this was the mystery compound added to the container with the higher boiling point.
Note that C6H12O6 is the formula for glucose, and will not ionize in solution.
Example Question #6 : Colligative Properties
The equation for boiling point elevation is written as 
The "
If a solution has ion pairing taking place, which statement is true?
The vapor pressure of the solution will be lower than predicted.
The molality of the solution will decrease.
The actual boiling point elevation will be lower than the theoretical boiling point elevation.
The solute will not raise the boiling point of the solution.
The actual boiling point elevation will be lower than the theoretical boiling point elevation.
If there is ion pairing taking place in a solution, the van't Hoff factor will be slightly lower than predicted. As a result, the boiling point will not be as elevated as it would be if all of the ions were separated from each other. This conclusion can be draw from the given equation, 
Example Question #701 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Which of the following aqueous solutions will have the highest boiling point?
2m MgCl2
2m NaCl
1m MgCl2
1m NaF
2m MgCl2
In order to answer this problem, consider the equation for boiling point elevation: 


Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Physical Resources