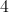All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #691 : Ssat Upper Level Quantitative (Math)
The base and height of a right triangle are each 1 inch. What is the hypotenuse?
You need to use the Pythagorean Theorem, which is 
Add the first two values and you get 

Example Question #1 : Apply The Pythagorean Theorem To Find The Distance Between Two Points In A Coordinate System: Ccss.Math.Content.8.G.B.8

Give the perimeter of the above parallelogram if 
By the 

The perimeter of the parallelogram is
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
A right triangle has legs with lengths of 






Using the numbers given to us by the question,

Example Question #411 : Grade 8
A right triangle has legs with the lengths 

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Example Question #2 : Apply The Pythagorean Theorem To Determine Unknown Side Lengths In Right Triangles: Ccss.Math.Content.8.G.B.7
Find the length of the hypotenuse in the right triangle below.

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse.
Example Question #141 : Geometry
If James traveled north 

The distances when put together create a right triangle.
The distance between them will be the hypotenuse or the diagonal side.
You use Pythagorean Theorem or 
So you plug 





Then you find the square root of each side and that gives you your answer of 
Example Question #692 : Ssat Upper Level Quantitative (Math)
If the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 20, and one of the legs is 12, what is the value of the other leg?
The triangle in this problem is a variation of the 3, 4, 5 right triangle. However, it is 4 times bigger. We know this because 

Therefore, the length of the other leg will be equal to:
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Height Of A Right Triangle
A given right triangle has a base of length 

Not enough information provided
For a given right triangle with base 



Therefore, to find the height 

Plugging in our values for 

Example Question #3 : How To Find The Height Of A Right Triangle
A given right triangle has a base length of 

Not enough information provided
For a given right triangle with base 



Therefore, to find the height 

Plugging in our values for 

Example Question #693 : Ssat Upper Level Quantitative (Math)
A given right triangle has a hypotenuse of 

Not enough information provided
Not enough information provided
For a given right triangle with base 



However, we have not been given a base or leg length for the right triangle, only the length of the hypotenuse and the area. We therefore do not have enough information to solve for the height 
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources