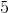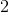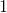All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #61 : Data Analysis / Probablility

The above set of balls is placed in a box. Give the probability that, if a ball is drawn at random, it will be a gray ball marked with a number that is a multiple of 3.
Of the twenty-five balls in the box, five are both gray and marked with a number that is a multiple of 3 (3, 6, 90), as seen in the figure below:

This makes the probability of drawing one of these balls

Example Question #1691 : Ssat Upper Level Quantitative (Math)

Above is a part of the board for a popular board game. Terry is moving clockwise on the board; his playing piece is represented by the black triangle. He is about to roll a pair of fair six-sided dice. He collects $10,000 every time he lands on or passes the space marked "Onward!"
What are the odds in favor of, or against, him collecting $10,000 on this turn?
5 to 1 in favor
11 to 1 in favor
5 to 1 against
11 to 1 against
11 to 1 in favor
Terry will collect $10,000 if he rolls a four or higher. As can be seen in the diagram below, out of thirty-six equally probable outcomes possible with the roll of two fair six-sided dice, there are only three rolls unfavorable to this outcome, and thirty-three favorable:

This makes the odds

Example Question #62 : Data Analysis / Probablility
In the game of Crazy Eights, which is played with an ordinary deck of 52 playing cards, each player lays down a card from his hand on top of a discard pile according to the card that has previously been played. The card he is allowed to play must be a card of the same rank or suit, or it must be an eight of any suit.
At the beginning of the hand, the seven of diamonds was turned over; Kenny, who was first, played a six of diamonds on top of it. Dick, who plays next, has the following cards in his hand:
As can be seen, Dick does not have a playable card. By the rules, he must draw a card, and, if he can play it, he must. What is the probability that the card he draws will be playable?
Dick knows 10 of the cards the deck - the eight in his hand, and the two in the discard pile. Of the other 
The four eights;
The other three sixes (hearts, clubs, spades); and,
The other ten diamonds (the six and the seven have been played, and the eight of diamonds has already been counted).
This makes
of the 42 cards playable, so the probability that a playable card will be drawn is 
Example Question #31 : Outcomes
In the game of Crazy Eights, which is played with an ordinary deck of 52 playing cards, each player lays down a card from his hand on top of a discard pile according to the card that has previously been played. The card he is allowed to play must be a card of the same rank or suit, or it must be an eight of any suit.
At the beginning of the hand, the two of clubs has been turned over. Brenda has in her hand eight cards, as follows:
As can be seen, Brenda cannot play a card. By the rules, she must draw a card, and, if she can play it, she must. What is the probability that the card she draws will be playable?
Brenda knows nine of the cards - the one in the discard pile and the eight in her hand. Therefore, the next card can be one of 
The four eights;
The other three twos (hearts, spades, diamonds); and,
The other eleven clubs (the two has been played, and the eight of diamonds has already been counted).
This makes
of the 42 cards playable, so the probability that a playable card will be drawn is 
Example Question #61 : Data Analysis / Probablility
In a jar, there are 3 blue marbles, 5 red marbles, 8 green marbles. If Bob reaches his hand in a jar, and grabs one marble, what is the likelihood he will pick up a blue marble?
First, calculate the total number of marbles in the jar, which is 

Example Question #32 : Probability
A fair six-sided die has on its faces the numbers 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3; a fair eight-sided die has on its faces the numbers 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4. If both dice are rolled, what is the probability that the numbers add up to 3 or less?
In order for the roll to add up to 3 or less, neither die can come up 3 or 4. Therefore, we look at the probabilities that each die can come up 1 and 2.
The six-sided die comes up 1 with probability 

The six-sided die comes up 1 with probability 

A roll of 3 or less can happen three ways:
Case 1: Both dice come up 1. The probability of this, by the Multiplication Principle, is
Case 2: The six-sided die comes up 1 and the eight-sided die comes up 2. The probability of this, by the Multiplication Principle, is
Case 3: The six-sided die comes up 2 and the eight-sided die comes up 1. The probability of this, by the Multiplication Principle, is
These are mutually exclusive events, so add these probabilities:
Example Question #1 : Inferences And Trends
Looking at the following data set, would this distribution be normally distributed, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right?
Normally distributed
Skewed to the right
Skewed to the left
Skewed to the right
The data has two large outliers that are to high compare to the rest of the data. That means they fall far to the right of the distribution. This leads to a right tail for the data curve and that makes it skewed to the right.
Example Question #1 : How To Recognize A Trend

Jim counted the number of visitors he had each day for a period. The graph provided shows the amount of days that he got 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 visitors. After looking at the data, what is the mode amount of visits?
The mode of a bar chart is the bar that is the tallest since it is the one that occurs the most.

In this data set, 

All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources