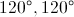All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #488 : Geometry
A given right triangle has legs of lengths and , respectively. What is the area of the right triangle?
Not enough information available
The area of a right triangle with a base and a height can be found with the formula . Since the two legs of a right triangle are perpendicular to each other, we can use these as the base and height in the formula. Therefore:
Example Question #489 : Geometry
The lengths of the hypotenuses of ten similar right triangles form an arithmetic sequence. The smallest triangle has legs of lengths 3 and 4 inches; the second-smallest triangle has a hypotenuse of length one foot.
Which of the following responses comes closest to the area of the largest triangle?
5 square feet
9 square feet
8 square feet
7 square feet
6 square feet
8 square feet
The hypotenuse of the smallest triangle can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem:
inches.
Let be the lengths of the hypotenuses of the triangles in inches. and , so their common difference is
The arithmetic sequence formula is
The length of the hypotenuse of the largest triangle - the tenth triangle - can be found by substituting :
inches.
The largest triangle has hypotenuse of length 68 inches. Since the triangles are similar, corresponding sides are in proportion. If we let and be the lengths of the legs of the largest triangle, then
Similarly,
The area of a right triangle is half the product of its legs:
square inches.
Divide this by 144 to convert to square feet:
Of the given responses, 8 square feet is the closest, and is the correct choice.
Example Question #490 : Geometry

Figure NOT drawn to scale
In the above figure, is a right triangle. , , . What fraction of has been shaded in?
The length of the leg , which we will call , can be calculated by setting , the length of hypotenuse , and , the length of leg , and applying the Pythagorean Theorem:
.
Construct the altitude of - which is also that of , the shaded region - from to . We call the length of this altitude (height). The figure is seen below.

The area of is one half this height multiplied by the corresponding base length :
The area of , the shaded region - is, similarly,
Therefore, the fraction that is of is the fraction of their areas:
Substituting the measures of the two segments:
Example Question #491 : Geometry
What is the area of a right triangle whose hypotenuse is 13 inches and whose legs each measure a number of inches equal to an integer?
It cannot be determined from the information given.
We are looking for a Pythagorean triple - that is, three integers that satisfy the relationship . We know that , and the only Pythagorean triple with is . The legs of the triangle are therefore 5 and 12, and the area of the right triangle is
Example Question #1 : How To Find If Right Triangles Are Congruent
Given:
, where is a right angle; ;
, where is a right angle and ;
, where is a right angle and has perimeter 60;
, where is a right angle and has area 120;
, where is a right triangle and
Which of the following must be a false statement?
All of the statements given in the other responses are possible
has as its leg lengths 10 and 24, so the length of its hypotenuse, , is
Its perimeter is the sum of its sidelengths:
Its area is half the product of the lengths of its legs:
and have the same perimeter and area, respectively, as ; also, between and , corresponding angles are congruent. In the absence of other information, none of these three triangles can be eliminated as being congruent to .
However, and . Therefore, . Since a pair of corresponding sides is noncongruent, it follows that .
Example Question #1 : How To Find If Right Triangles Are Congruent
Given: and with right angles and ; .
Which of the following statements alone, along with this given information, would prove that ?
I)
II)
III)
II or III only
III only
I or II only
Any of I, II, or III
I or III only
Any of I, II, or III
; since both are right angles.
Given that two pairs of corresponding angles are congruent and any one side of corresponding sides is congruent, it follows that the triangles are congruent. In the case of Statement I, the included sides are congruent, so by the Angle-Side-Angle Congruence Postulate, . In the case of the other two statements, a pair of nonincluded sides are congruent, so by the Angle-Angle-Side Congruence Theorem, . Therefore, the correct choice is I, II, or III.
Example Question #52 : Properties Of Triangles
, where is a right angle, , and .
Which of the following is true?
None of the statements given in the other choices is true.
has area 100
has perimeter 40
has area 100
, and corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent.
Since is a right angle, so is . and ; since , it follows that . is an isosceles right triangle; consequently, .
is a 45-45-90 triangle with hypotenuse of length . By the 45-45-90 Triangle Theorem, the length of each leg is equal to that of the hypotenuse divided by ; therefore,
is eliminated as the correct choice.
Also, the perimeter of is
.
This eliminates the perimeter of being 40 as the correct choice.
Also, is eliminated as the correct choice, since the triangle is 45-45-90.
The area of is half the product of the lengths of its legs:
The correct choice is the statement that has area 100.
Example Question #51 : Right Triangles
One angle of a right triangle has measure . Give the measures of the other two angles.
This triangle cannot exist.
This triangle cannot exist.
A right triangle must have one right angle and two acute angles; this means that no angle of a right triangle can be obtuse. But since , it is obtuse. This makes it impossible for a right triangle to have a angle.
Example Question #492 : Geometry
One angle of a right triangle has measure . Give the measures of the other two angles.
This triangle cannot exist.
One of the angles of a right triangle is by definition a right, or , angle, so this is the measure of one of the missing angles. Since the measures of the angles of a triangle total , if we let the measure of the third angle be , then:
The other two angles measure .
Example Question #52 : Right Triangles
Find the degree measure of in the right triangle below.

The total number of degrees in a triangle is .
While is provided as the measure of one of the angles in the diagram, you are also told that the triangle is a right triangle, meaning that it must contain a angle as well. To find the value of , subtract the other two degree measures from .
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources