All PSAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #22 : Rectangles

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale
Give the ratio of the perimeter of Rectangle 

The perimeter of Rectangle 
Opposite sides of a rectangle are congruent, so
and
The perimeter of Rectangle 
Opposite sides of a rectangle are congruent, so


and
The ratio of the perimeters is

Example Question #331 : Plane Geometry

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale
Refer to the above figure, which shows a rectangular garden (in green) surrounded by a dirt path (in orange) eight feet wide throughout. What is the area of that dirt path?
The correct area is not given among the other responses.
The dirt path can be seen as the region between two rectangles. The outer rectangle has length and width 100 feet and 60 feet, respectively, so its area is

The inner rectangle has length and width 


The area of the path is the difference of the two:

Example Question #652 : Geometry

Refer to the above figure, which shows a rectangular garden (in green) surrounded by a dirt path (in orange). The dirt path is seven feet wide throughout. Which of the following polynomials gives the area of the dirt path in square feet?
The area of the dirt path is the difference between the areas of the outer and inner rectangles.
The outer rectangle has area
The area of the inner rectangle can be found as follows:
The length of the garden is 

The width of the garden is 

The area of the garden is their product:
Now, subtract the areas:
Example Question #21 : How To Find The Area Of A Rectangle
Two circles of a radius of 

The area of a square =
The area of a circle is
Area = Area of Square 
Example Question #332 : Plane Geometry
If the area Rectangle A is 


Example Question #1 : Parallelograms
ABCD is a parallelogram. BD = 5. The angles of triangle ABD are all equal. What is the perimeter of the parallelogram?
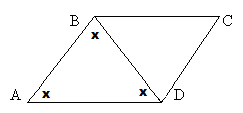
If all of the angles in triangle ABD are equal and line BD divides the parallelogram, then all angles in triangle BDC must be equal as well.
We now have two equilateral triangles, so all sides of the triangles will be equal.
All sides therefore equal 5.
5+5+5+5 = 20
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All PSAT Math Resources





















































