All Precalculus Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #81 : Pre Calculus
What is 
If you examine the unit circle, you'll see that the value of 

Example Question #21 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions
Which one of these is positive in quadrant III?
Tangent
No trig functions
All trig functions
Sine
Cosine
Tangent
The pattern for positive functions is All Student Take Calculus. In quandrant I, all trigonometric functions are positive. In quadrant II, sine is positive. In qudrant III, tangent is positive. In quadrant IV, cosine is positive.
Example Question #21 : Trigonometry
Find a coterminal angle for 
Coterminal angles are angles that, when drawn in the standard position, share a terminal side. You can find these angles by adding or subtracting 360 to the given angle. Thus, the only angle measurement that works from the answers given is 
Example Question #25 : Graphs And Inverses Of Trigonometric Functions
Which of the following angles is coterminal with 
Each angle given in the other choices is coterminal with 
Each angle given in the other choices is coterminal with 
For an angle to be coterminal with 







All four choices pass the test, so all four angles are coterminal with 
Example Question #1 : Trigonometric Operations
What is 
To get rid of 


Example Question #3 : Trigonometry
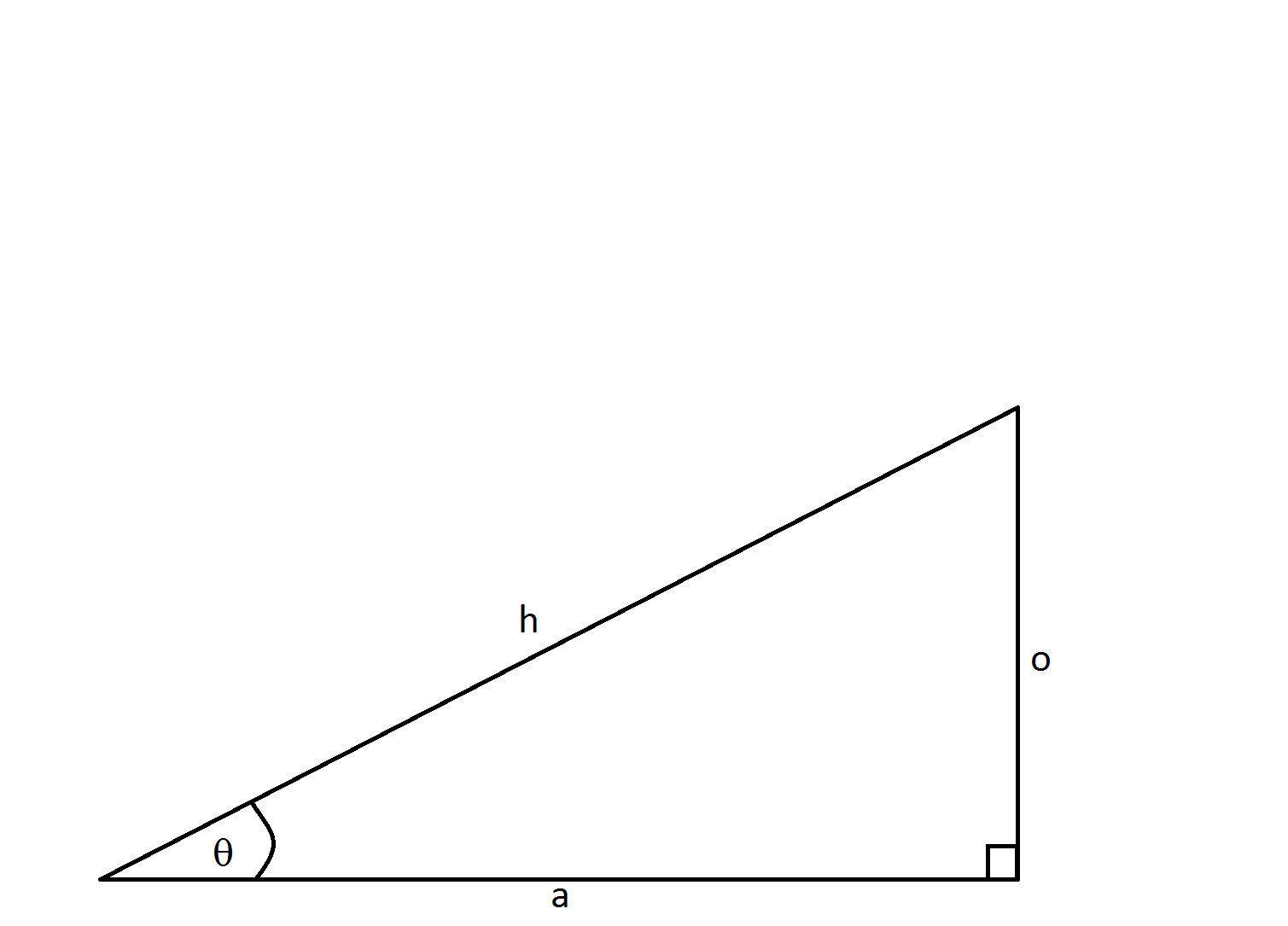
In order to find 



Now to find the measure of the angle using the 
If you calculated the angle's measure to be 
Example Question #82 : Pre Calculus
What is the amplitude of the following equation?
Based on the generic form 
Example Question #27 : Graphs And Inverses Of Trigonometric Functions
What is one possible length of side 



(Hint: There are two possible answers, but only one of them is listed.)
First we must set up our equation given the information.
Example Question #31 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions
How many 

![[0,5]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/214543/gif.latex)
The period of the sine function is 


The graph is below.

Example Question #31 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions
If 


It is a question of what quadrant 
A negative value for secant indicates quadrant II or III. Since secant is the reciprocal of cosine, the measurement includes the x value and the r value with regards to position.To get a negative value for secant or cosine we will need a negative x value and either a positive or negative y value to get the correct r value.
A positive value for cotangent indicates quadrant I or III. Since cotangent is the reciprocal of tangent, the measurement includes the x and y values with regards to the position. To get a cotangent that is positive we will need a positive x value and either a positive or negative y value.
The overlap between these two statements is quadrant III. Therefore, 
All Precalculus Resources







































































