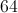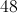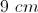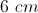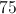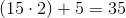All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #271 : Plane Geometry
This figure is a rhombus with a side of 8 in.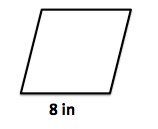
What is the perimeter of the rhombus (in)?
The perimeter of the rhombus is the distance around the outside of the figure. Since a rhombus has 4 congruent sides, the perimeter is simply 
Example Question #272 : Geometry
You are given a rhombus with a side of 






A rhombus is a quadrilateral (



Example Question #1 : Triangles
An isosceles triangle has a base of 


Example Question #1 : Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangles
One side of an acute isosceles triangle is 15 feet. Another side is 5 feet. What is the perimeter of the triangle in feet?
Because this is an acute isosceles triangle, the third side must be the same as the longer of the sides that you were given. To find the perimeter, multiply the longer side by 2 and add the shorter side.
Example Question #273 : Geometry
An isoceles triangle has a base angle five more than twice the vertex angle. What is the difference between the base angle and the vertex angle?
A triangle has 180 degrees. An isoceles triangle has one vertex angle and two congruent base angles.
Let 

So the equation to solve becomes

So the vertex angle is 

Example Question #1421 : Concepts
Points A and B lie on a circle centered at Z, where central angle <AZB measures 140°. What is the measure of angle <ZAB?
20°
15°
30°
25°
Cannot be determined from the given information
20°
Because line segments ZA and ZB are radii of the circle, they must have the same length. That makes triangle ABZ an isosceles triangle, with <ZAB and <ZBA having the same measure. Because the three angles of a triangle must sum to 180°, you can express this in the equation:
140 + 2x = 180 --> 2x = 40 --> x = 20
Example Question #271 : Plane Geometry
Triangle FGH has equal lengths for FG and GH; what is the measure of ∠F, if ∠G measures 40 degrees?
70 degrees
None of the other answers
100 degrees
140 degrees
40 degrees
70 degrees
It's good to draw a diagram for this; we know that it's an isosceles triangle; remember that the angles of a triangle total 180 degrees.
Angle G for this triangle is the one angle that doesn't correspond to an equal side of the isosceles triangle (opposite side to the angle), so that means ∠F = ∠H, and that ∠F + ∠H + 40 = 180,
By substitution we find that ∠F * 2 = 140 and angle F = 70 degrees.
Example Question #2 : Triangles
The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is 
An isosceles triangle has two congruent base angles and one vertex angle. Each triangle contains 



Example Question #1421 : Concepts
In an isosceles triangle the base angle is five less than twice the vertex angle. What is the sum of the vertex angle and the base angle?
Every triangle has 180 degrees. An isosceles triangle has one vertex angle and two congruent base angles.
Let 
and 
So the equation to solve becomes
or
Thus the vertex angle is 38 and the base angle is 71 and their sum is 109.
Example Question #1 : Triangles
Sides 



This triangle has an angle of 




Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources