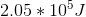All AP Physics 2 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #321 : Ap Physics 2
Describe the pressure versus volume graph for an isobaric process, where 
Linear -
Cubic -
Vertical line -
Horizontal line -
Quadratic -
Horizontal line -
For an isobaric process, the pressure is constant. Therefore, on a P-V diagram, the object will have the same pressure. Since pressure is on the y-axis, that means that we will have a straight horizontal line at the initial pressure.
Example Question #2 : Other Thermodynamics Concepts
Describe the graph of an isochoric process, where 
Vertical line -
Horizontal line -
Cubic -
Linear, going through origin -
Quadratic -
Horizontal line -
For an isochoric process, the volume remains constant. Therefore, in a P-V diagram, for every pressure, we will have the same volume. Since volume is on the 

Example Question #1 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
In the cylinder of a certain internal combustion engine, the hot gas caused by the combustion of the fuel expands from 


Work is defined as pressure times change in volume for constant pressure cases. Work done on the gas takes a positive sign in the AP equation sheet, and the equation for work is given with a negative sign. This question asks for work on the piston, not on the gas (or "system" in AP parlance), and since the force and displacement are in the same direction for the piston, it has positive work done on it, increasing its kinetic energy.
Example Question #2 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
Suppose that a sample of an ideal, monatomic gas containing 

For this question, we're given the amount of gas (in moles) as well as the temperature of the gas (in Kelvin) and we're being asked to determine the internal energy of this gas.
It's important to recall that internal energy is a microscopic (as opposed to macroscopic) measurement of the energy of a system. The internal energy of a system includes the kinetic energy of the individual atoms or molecules, which can be caused by translational motion, vibrational motion, and rotational motion. In addition, the internal energy also includes any potential energy that results from intermolecular interactions between the atoms or molecules.
We're told in the question stem that the gas under consideration is both ideal as well as monatomic. Because it is ideal, we can assume that there is no significant intermolecular interactions between the gas particles, which therefore means that there is no need to worry about the potential energy component of internal energy. Moreover, we're told that the gas under consideration is monatomic, which means that the kinetic energy component of internal energy is only caused by translational motion; in other words, we can neglect vibrational and rotational contributions to kinetic energy.
The significance of all this is that we can relate the internal energy of this gas solely to the translational motion. Thus, we'll need to use an expression that relates the variables given in the question stem.
The above expression tells us that the total internal energy, 
If we plug in the quantities given in the question stem, we find our answer.
Example Question #1 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
A piston is filled with methane at a pressure of 

Since the problem statement tells us that this is an isobaric process, we can use the following expression:
The statement also tells us that we start with 2L of gas and end up with double that amount, or 4L. Therefore, the change in volume is 2L. Plugging this and our pressure into the above expression, we get:
However, these units are not compatible, so we need to do some unit analysis:
Example Question #4 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy




Since the problem statement tells us that the gas expands at a constant temperature, we can use the expression for isothermal expansion:
We have all of these values, so it's just important that we choose the correct gas constant. Since we are working with joules and Kelvin, we will use:
Plugging in values for each variable:
Example Question #5 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
How much heat does it take to bring 

Use the following values for ethanol in your calculations:
There are two calculations that we will need to perform to calculate the total energy needed. The first is the energy needed to bring the ethanol to its boiling point. Then, the energy needed to bring the ethanol to its saturated vapor state, which simply means that all of the ethanol has vaporized but is still at it's boiling point temperature. So, we will first calculate how much energy is needed to bring the ethanol to its boiling point:
Now we need to calculate the energy it takes to vaporize all of the ethanol:
Now adding these together:
Example Question #6 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
A system absorbs heat 

Heat is absorbed so that is a 


Example Question #7 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
Determine the energy needed to bring a rigid metal can of volume 


None of these
Energy due to a compressed gas:
Plugging in values:
Converting units:
Example Question #8 : Work, Enthalpy, And Internal Energy
A gas with a fixed number of molecules has 

It decreases by
It decreases by
It does not change
It increases by
It increases by
It increases by
Since 




Certified Tutor
All AP Physics 2 Resources