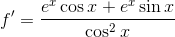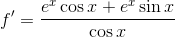All AP Calculus AB Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #35 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Differentiate
The function is a product of the functions 

The derivative in the first term is 
The derivative in the second term required the use of the chain rule. First we write the derivative of 





Therefore,
Example Question #36 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the following equation:
Given that there are 2 terms in the numerator and only one in the denominator, one can split up the equation into 2 separate derivatives:

Now we simplify these, and proceed to solve:
Example Question #37 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the following equation:
None of the other answers.
Because this problem contains two functions multiplied together that can't be simplified any further, it calls for the product rule, which states that![]()
By applying this rule to the equation

we get
Example Question #38 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the following function:
None of the other answers
Because we are dealing with a quotient that cannot be simplified, we use the quotient rule, which states that if


By observing the given equation

we can see that

and

Therefore, the derivative is

Example Question #39 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the following equation:
None of the other answers.
Because we are differentiating a quotient that cannot be simplified, we must use the quotient rule, which states that if

then

By observing the given equation,

we see that in this case,

and

Given this information, the quotient rule tells us that

Example Question #40 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the following equation:
None of the other answers.
This problem is a quotient rule inside of a chain rule. First, let's look at the chain rule:
![]() .
.
Given this, we can deduce that since


and

By plugging these into the chain rule formula, we get

To find the derivative of the
second term, we must use the quotient rule, which states that the the derivative
of a quotient is ((denominator)(derivative of numerator)-(numerator)(derivative
of denominator))/(denominator squared). Using this rules we find that

By plugging this back in, we find the final derivative to be
Example Question #41 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the function:
The derivative of the function is equal to
and was found using the following rules:


Example Question #42 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the function
To find the derivative of a quotient, you apply the quotient rule:
In our case, we have 
Using the function from the problem statement and taking its derivative, we get
Example Question #43 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the function
To find the derivative of a quotient, you apply the quotient rule:
In our case, we have 
Using the function from the problem statement and taking its derivative, we get
Example Question #44 : Derivative Rules For Sums, Products, And Quotients Of Functions
Find the derivative of the function
To find the derivative of the function, you must apply the product rule. The product rule is as follows
In the first part of the expression, we have 


Using the product rule from above, we have
All AP Calculus AB Resources