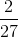All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2931 : Isee Lower Level (Grades 5 6) Quantitative Reasoning
Solve:
Example Question #1891 : Numbers And Operations
Solve:
Example Question #261 : Number & Operations With Fractions
Solve:
Example Question #262 : Number & Operations With Fractions
Solve:
Example Question #814 : Fractions
Solve the following:
Example Question #263 : Number & Operations With Fractions
Solve:
Example Question #71 : Interpret The Product (A/B) × Q As A Part Of A Partition Of Q Into B Equal Parts: Ccss.Math.Content.5.Nf.B.4a
Jessica made 

A keyword in our question that gives us a clue that we are going to multiply to solve this problem is the word "of". 
We know that we have 




Example Question #1 : Interpret The Product (A/B) × Q As A Part Of A Partition Of Q Into B Equal Parts: Ccss.Math.Content.5.Nf.B.4a
Ronda made 

A keyword in our question that gives us a clue that we are going to multiply to solve this problem is the word "of". 
We know that we have 




Example Question #1903 : Numbers And Operations
Mary-Beth made 

A keyword in our question that gives us a clue that we are going to multiply to solve this problem is the word "of". 
We know that we have 




Example Question #1 : Interpret The Product (A/B) × Q As A Part Of A Partition Of Q Into B Equal Parts: Ccss.Math.Content.5.Nf.B.4a
Alison made 

A keyword in our question that gives us a clue that we are going to multiply to solve this problem is the word "of". 
We know that we have 




Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources








 can be reduced by dividing both sides by
can be reduced by dividing both sides by 








 can be reduced by dividing both sides by
can be reduced by dividing both sides by