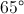All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #771 : Ssat Upper Level Quantitative (Math)

Figure NOT drawn to scale.
If and , evaluate .
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so
Example Question #16 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
If the vertex angle of an isoceles triangle is , what is the value of one of its base angles?
In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are the same. Also, the three angles of a triangle add up to .
So, subtract the vertex angle from . You get .
Because there are two base angles you divide by , and you get .
Example Question #2 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
Refer to the above diagram.
Which of the following could be a measure of ?
All of the other choices give a possible measure of .
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so
.
We also have the following constraints:
Then, by the addition property of inequalities,
Therefore, the measure of must fall in that range. Of the given choices, only falls in that range.
Example Question #3 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle

Refer to the above diagram.
Which of the following could be a measure of ?
All of the other responses are correct.
All of the other responses are correct.
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so
or
Therefore, the maximum value of is the least possible value of subtracted from the greatest possible value of :
The minimum value of is the greatest possible value of subtracted from the least possible value of :
Therefore,
Since all of the choices fall in this range, all are possible measures of .
Example Question #4 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Find the angle measurement of .

All the angles in a triangle must add up to .
Example Question #111 : Properties Of Triangles
Find the angle measurement of .

All the angles in a triangle must add up to
Example Question #112 : Properties Of Triangles
Find the angle measurement of .

All the angles in a triangle must add up to .
Example Question #113 : Properties Of Triangles
An isosceles triangle has an angle whose measure is .
What could be the measures of one of its other angles?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(a) or (c) only
(b) only
(a) only
(c) only
(a), (b), or (c)
(a), (b), or (c)
By the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, an isosceles triangle has two congruent interior angles. There are two possible scenarios if one angle has measure :
Scenario 1: The other two angles are congruent to each other. The degree measures of the interior angles of a triangle total , so if we let be the common measure of those angles:
This makes (b) a possible answer.
Scenario 2: One of the other angles measures also, making (c) a possible answer. The degree measure of the third angle is
,
making (a) a possible answer. Therefore, the correct choice is (a), (b), or (c).
Example Question #114 : Properties Of Triangles
One of the interior angles of a scalene triangle measures . Which of the following could be the measure of another of its interior angles?
A scalene triangle has three sides of different measure, so, by way of the Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, each angle is of different measure as well. We can therefore eliminate immediately.
Also, if the triangle also has a angle, then, since the total of the degree measures of the angles is , it follows that the third angle has measure
.
Therefore, the triangle has two angles that measure the same, and can be eliminated.
Similarly, if the triangle also has a angle, then, since the total of the degree measures of the angles is , it follows that the third angle has measure
.
The triangle has two angles that measure . This choice can be eliminated.
can be eliminated, since the third angle would have measure
,
an impossible situation since angle measures must be positive.
The remaining possibility is . This would mean that the third angle has measure
.
The three angles have different measures, so the triangle is scalene. is the correct choice.
Example Question #5 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Given: with . Locate on so that is the angle bisector of . What is ?

Above is the figure described.
The measures of the interior angles of a triangle total , so the measure of is
Since bisects this angle,
and
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources