All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #5 : Sectors

Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, circle C has a radius of 18, and the measure of angle ACB is equal to 100°. What is the perimeter of the red shaded region?
36 + 20π
36 + 10π
36 + 36π
18 + 36π
18 + 10π
36 + 10π
The perimeter of any region is the total distance around its boundaries. The perimeter of the shaded region consists of the two straight line segments, AC and BC, as well as the arc AB. In order to find the perimeter of the whole region, we must add the lengths of AC, BC, and the arc AB.
The lengths of AC and BC are both going to be equal to the length of the radius, which is 18. Thus, the perimeter of AC and BC together is 36.
Lastly, we must find the length of arc AB and add it to 36 to get the whole perimeter of the region.
Angle ACB is a central angle, and it intercepts arc AB. The length of AB is going to equal a certain portion of the circumference. This portion will be equal to the ratio of the measure of angle ACB to the measure of the total degrees in the circle. There are 360 degrees in any circle. The ratio of the angle ACB to 360 degrees will be 100/360 = 5/18. Thus, the length of the arc AB will be 5/18 of the circumference of the circle, which equals 2πr, according to the formula for circumference.
length of arc AB = (5/18)(2πr) = (5/18)(2π(18)) = 10π.
Thus, the length of arc AB is 10π.
The total length of the perimeter is thus 36 + 10π.
The answer is 36 + 10π.
Example Question #71 : Intermediate Geometry

In the circle above, the angle A in radians is
What is the length of arc A?
Circumference of a Circle =
Arc Length
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of An Arc
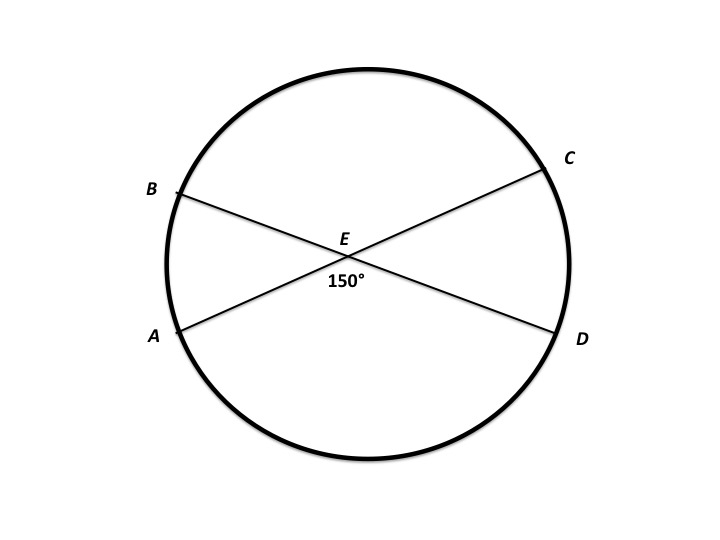
In the figure above, 




The formula for arclength is 
You know that 



Since

the sum the lengths of arcs 


Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of An Arc

Figure NOT drawn to scale
Refer to the above figure. Evaluate 


Setting 

Example Question #21 : Circles
A pie has a diameter of 12". A piece is cut out, having a surface area of 4.5π. What is the angle of the cut?
4.5°
45°
25°
90°
12.5°
45°
This is simply a matter of percentages. We first have to figure out what percentage of the surface area is represented by 4.5π. To do that, we must calculate the total surface area. If the diameter is 12, the radius is 6. Don't be tricked by this!
A = π * 6 * 6 = 36π
Now, 4.5π is 4.5π/36π percentage or 0.125 (= 12.5%)
To figure out the angle, we must take that percentage of 360°:
0.125 * 360 = 45°
Example Question #271 : Plane Geometry
Eric is riding a Ferris wheel. The Ferris wheel has 18 compartments, numbered in order clockwise. If compartment 1 is at 0 degrees and Eric enters compartment 13, what angle is he at?
180
240
260
300
280
240
12 compartments further means 240 more degrees. 240 is the answer.
360/12 = 240 degrees
Example Question #11 : Plane Geometry
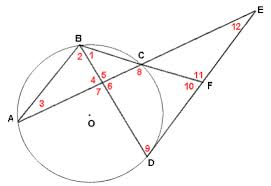
In the figure above that includes Circle O, the measure of angle BAC is equal to 35 degrees, the measure of angle FBD is equal to 40 degrees, and the measure of arc AD is twice the measure of arc AB. Which of the following is the measure of angle CEF? The figure is not necessarily drawn to scale, and the red numbers are used to mark the angles, not represent angle measures.
The measure of angle CEF is going to be equal to half of the difference between the measures two arcs that it intercepts, namely arcs AD and CD.
Thus, we need to find the measure of arcs AD and CD. Let's look at the information given and determine how it can help us figure out the measures of arcs AD and CD.
Angle BAC is an inscribed angle, which means that its meausre is one-half of the measure of the arc that it incercepts, which is arc BC.
Thus, since angle BAC is 35 degrees, the measure of arc BC must be 70 degrees.
We can use a similar strategy to find the measure of arc CD, which is the arc intercepted by the inscribed angle FBD.
Because angle FBD has a measure of 40 degrees, the measure of arc CD must be 80 degrees.
We have the measures of arcs BC and CD. But we still need the measure of arc AD. We can use the last piece of information given, along with our knowledge about the sum of the arcs of a circle, to determine the measure of arc AD.
We are told that the measure of arc AD is twice the measure of arc AB. We also know that the sum of the measures of arcs AD, AB, CD, and BC must be 360 degrees, because there are 360 degrees in a full circle.
Because AD = 2AB, we can substitute 2AB for AD.
This means the measure of arc AB is 70 degrees, and the measure of arc AD is 2(70) = 140 degrees.
Now, we have all the information we need to find the measure of angle CEF, which is equal to half the difference between the measure of arcs AD and CD.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Angle Of A Sector
The length of an arc, 





The circumference of the circle is 
The length of the arc S is 
A ratio can be established:
Solving for 
Note: This makes sense. Since the arc S was one-fourth the circumference of the circle, the central angle formed by arc S should be one-fourth the total degrees of a circle.
Example Question #13 : Plane Geometry
In the circle above, the length of arc BC is 100 degrees, and the segment AC is a diameter. What is the measure of angle ADB in degrees?
100
40
90
80
cannot be determined
40
Since we know that segment AC is a diameter, this means that the length of the arc ABC must be 180 degrees. This means that the length of the arc AB must be 80 degrees.
Since angle ADB is an inscribed angle, its measure is equal to half of the measure of the angle of the arc that it intercepts. This means that the measure of the angle is half of 80 degrees, or 40 degrees.
Example Question #521 : Act Math
What is the angle of a sector of area 


To begin, you should compute the complete area of the circle:
For your data, this is:
Now, to find the angle measure of a sector, you find what portion of the circle the sector is. Here, it is:
Now, multiply this by the total 
Rounded, this is 
All SAT Math Resources

































































