All SAT II Math I Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Understanding Domain And Range
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
The domain includes the values that go into a function (the x-values) and the range are the values that come out (the 


Example Question #1 : Domain And Range
Which of the following is NOT a function?
A function has to pass the vertical line test, which means that a vertical line can only cross the function one time. To put it another way, for any given value of 












Example Question #3 : How To Find The Domain Of A Function
Give the domain of the function below.

The domain is the set of possible value for the 

Now we can solve for 
There is no real value of 
The radicand is always positive, and 


Example Question #3 : How To Factor The Quadratic Equation
Find the domain:
To find the domain, find all areas of the number line where the fraction is defined.

Factor by finding two numbers that sum to -2 and multiply to 1. These numbers are -1 and -1.
Example Question #1 : Functions And Graphs
If 

Using 



Therefore 

Example Question #32 : Functions And Graphs
What is the range of the function?
This function is a parabola that has been shifted up five units. The standard parabola has a range that goes from 0 (inclusive) to positive infinity. If the vertex has been moved up by 5, this means that its minimum has been shifted up by five. The first term is inclusive, which means you need a "[" for the beginning.
Minimum: 5 inclusive, maximum: infinity
Range:
Example Question #3 : Functions And Graphs
What is the domain of the function?
The domain represents the acceptable 
Minimum: 0 inclusive, maximum: infinity
Domain:
Example Question #3 : Domain And Range
What is the domain of the function?
The domain of a function refers to the viable 
This function does not have any such restrictions; any value of 
Domain:
Example Question #11 : Range And Domain
What is the range of the function?
This function represents a parabola that has been shifted 15 units to the left and 2 units up from its standard position.
The vertex of a standard parabola is at (0,0). By shifting the graph as described, the new vertex is at (-15,2). The 
Minimum: 2 (inclusive), maximum: infinity
Range:
Example Question #12 : Range And Domain
What is the domain of the function?

The domain of a function refers to the viable 
Let's start with the radical, which must be greater than or equal to zero:
Next, we will look at the fraction denominator, which cannot equal zero:
Our final answer will be the union of the two sets.
Minimum: 2 (inclusive), maximum: infinity
Exclusion: 22
Domain:
All SAT II Math I Resources

 is a sine curve. What are the domain and range of this function?
is a sine curve. What are the domain and range of this function?























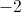

















![[0,100]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/218211/gif.latex)


![(-\infty,3]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/218220/gif.latex)

![(-3,5]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/218221/gif.latex)






















