All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Gibbs Free Energy
For Constant Temperature, Gibbs Free Energy is defined as:
Where , 



Which of the following scenarios is not possible?
The following condition is not possible:
This is because if enthalpy is positive, and entropy is negative, the negative sign in front of the temperature term in the formula becomes positive. Addition of 2 positive numbers can not be negative. Plugging in arbitrary numbers into the other conditions can show they are all possible.
Take the following condition:

Then Gibbs free energy 

Example Question #2 : Gibbs Free Energy
For constant temperature, Gibbs free energy is defined as:
Where , 


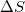
Given that a system is spontaneous, which of the following states are possible?
I.
II.
III.
IV.
IV only
I, II, III, and IV
II and III
I and III
I, II, and III
I and III
Condition I is always true. Condition II is never true, as Gibbs free energy cannot be negative if enthalpy is positive and entropy is negative. Condition III may be true if temperature is very high (this is the scenario when the 



Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
The enthalpy of a reaction is 


Cannot be determined from the given information
Cannot be determined from the given information
Gibbs free energy of a system can be solved using the following equation.
where 




Example Question #1 : Thermodynamics
In an exergonic reaction, products will have __________ Gibbs free energy and the reaction is __________.
higher . . . spontaneous
lower . . . spontaneous
lower . . . nonspontaneous
higher . . . nonspontaneous
lower . . . spontaneous
Exergonic reaction suggests that the Gibbs free energy is negative. Since the change in Gibbs free energy is defined as Gibbs free energy of products - Gibbs free energy of reactants, a negative change in Gibbs free energy suggests that the products have a lower Gibbs free energy than reactants. A reaction is spontaneous if it has negative Gibbs free energy; therefore, exergonic reactions are always spontaneous. This is because the reaction is producing a more stable product (lower energy) from a less stable reactant (higher energy).
Example Question #2 : Thermodynamics
Which of the following is true regarding enthalpy and entropy?
The enthalpy of liquid water is nonzero whereas enthalpy of hydrogen gas is zero
The entropy of liquid water is higher than the entropy of hydrogen gas
Both of these are true
None of these are true
The enthalpy of liquid water is nonzero whereas enthalpy of hydrogen gas is zero
Enthalpy is the amount of internal energy contained in a compound whereas entropy is the amount of intrinsic disorder within the compound. Enthalpy is zero for elemental compounds such hydrogen gas and oxygen gas; therefore, enthalpy is nonzero for water (regardless of phase). Entropy, or the amount of disorder, is always highest for gases and lowest for solids. This is because gas molecules are widely spread out and, therefore, are more disordered than solids and liquids. Hydrogen gas will have a higher entropy than liquid water.
Example Question #1 : Thermodynamics
According to the law of thermodynamics, which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
I. Enthalpy of a system is always increasing
II. Entropy of a system is always increasing
III. Absolute entropy can never be negative
III only
II and III
II only
I and II
III only
The first law of thermodynamics states that the energy of the universe is always constant, which implies that energy cannot be created or destroyed. The energy lost by a system is gained by surroundings and vice versa; however, the total energy of the universe is always constant. The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy, or the amount of disorder in the universe, is always increasing. This suggests that the universe is always going towards a more disordered state. Based on these two laws, we can determine that statement I and statement II are false. Note that these two statements are talking about the system, rather than the universe. The energy (in the form of enthalpy) and entropy can increase or decrease in a system. The surroundings will compensate accordingly to keep the energy of universe constant and increase the entropy. Absolute entropy of a system, surroundings or the universe can never be negative because it isn’t possible to have negative disorder (this is due to the definition of entropy; just remember that entropy can never be negative). Note that the change in entropy can, however, be negative.
Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
A newly discovered element has been determined to have a standard entropy of 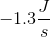
Second Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Equivalent Exchange
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics
Third Law of Thermodynamics
Third Law of Thermodynamics
The Third Law of Thermodynamics states that a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero has an entropy of 
where 
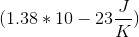
If only one microstate exists for the system, then the entropy is zero 
Remark: keep in mind that entropy changes can be negative, but the entropy of pure compounds cannot be negative.
Example Question #3 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
A chemical reaction is run in which 

The First Law of thermodynamics states that for a system that only exchanges energy by heat or work:
Work is done by the system, therefore
Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
An automobile engine provides 

The First Law of thermodynamics states that for a system that only exchanges energy by heat or work:
The heat is given off by the system, so 

Example Question #2 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
A chemical reaction is run in which 

The First Law of thermodynamics states that for a system that only exchanges energy by heat or work:
Heat is absorbed by the system, therefore

So

Certified Tutor
All Physical Chemistry Resources












































