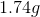All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2 : Galvanic And Electrolytic Cells
The Gibbs free energy of a redox reaction is __________ for a galvanic cell and is __________ for an electrolytic cell.
negative . . . positive
positive . . . positive
positive . . . negative
negative . . . negative
negative . . . positive
Gibbs free energy is the “free” energy available that can be used to perform useful work. A negative Gibbs free energy corresponds to a spontaneous reaction, whereas a positive Gibbs free energy corresponds to a nonspontaneous reaction. Recall that a galvanic cell involves a spontaneous reaction, whereas an electrolytic cell involves a nonspontaneous reaction; therefore, the Gibbs free energy of the reaction is negative for a galvanic cell and positive for an electrolytic cell.
Example Question #3 : Galvanic And Electrolytic Cells
What type of energy input is required for a galvanic cell?
Chemical energy
Electrical energy
Both electrical and chemical energy
Galvanic cells do not require energy
Galvanic cells do not require energy
Recall that galvanic cells carry out spontaneous reactions; therefore, they do not require energy. They release free energy that can be used to do work such as powering an electrical device (like cell phones).
Electrolytic cells, on the other hand, require energy because they carry out nonspontaneous reactions. They require the input of electrical energy.
Example Question #4 : Galvanic And Electrolytic Cells
Listed below are standard reduction potentials for a few elements.
Lithium:
Iron (with 
Aluminum:
Given this information, which of the following redox reactions can be found in a galvanic cell?
I.
II.
III.
I and III
III only
I only
I and II
I and II
Galvanic cells are electrochemical cells that are characterized by a spontaneous redox reaction. To solve this question, we need to find the standard potential for each of the given reactions. Note that each reaction is a redox reaction; therefore, there is an oxidation half-reaction and a reduction half-reaction for each one.
The first reaction has a ferrous ion being reduced (gaining electrons) and lithium being oxidized (losing electrons). From the given information, we can deduce the standard potential for each half-reaction. The standard potential for reduction of iron is 

Since its standard reaction potential is positive, this reaction is spontaneous and occurs in a galvanic cell.
The second reaction has aluminum being oxidized (


The third reaction has a lithium ion being reduced (


Example Question #171 : Physical Chemistry
What will happen when the two given half-cells are connected by a salt bridge to form a galvanic cell?


No reaction will take place.
Copper metal will be oxidized at the cathode; lead ions will be reduced at the anode.
Lead metal will be oxidized at the anode; copper ions will be reduced at the cathode.
Copper metal will be oxidized at the anode; lead ions will be reduced at the cathode.
Lead metal will be oxidized at the cathode; copper ions will be reduced at the anode.
Lead metal will be oxidized at the anode; copper ions will be reduced at the cathode.

Example Question #6 : Galvanic And Electrolytic Cells


For an electrolytic cell containing the two half-cells shown, the __________ reaction will take place and the 
nonspontaneous . . .
nonspontaneous . . .
spontaneous . . .
nonspontaneous . . .
spontaneous . . .
nonspontaneous . . .
In an electrolytic cell, the non-spontaneous reaction occurs. This means that Na is reduced (making it the cathode) and Mn is oxidized (making it the anode). The standard cell potential can then be calculated as follows:
Example Question #171 : Physical Chemistry
A battery converts __________ energy to __________ energy.
electrical . . . kinetic
chemical . . . kinetic
chemical . . . electrical
electrical . . . chemical
chemical . . . electrical
Electronic devices such as cell phones utilize batteries for power. A discharging battery converts the chemical energy associated with redox reactions to electrical energy that can be utilized to power the device. Kinetic energy is the energy associated with motion and is irrelevant to this question.
Example Question #171 : Physical Chemistry
Which of the following statements about a charging battery is true?
The reaction occurring is exothermic
The battery behaves as a galvanic cell
The Gibbs free energy of the reaction in the battery is positive
Oxidation occurs at the cathode and reduction occurs at anode
The Gibbs free energy of the reaction in the battery is positive
A charging battery behaves as an electrolytic cell. The process involves a nonspontaneous reaction; therefore, energy input is needed for charging a battery. This energy is provided by the electrical outlets that we use to charge our electronic devices, such as cell phones. Since it is nonspontaneous, the reaction occurring during charging has a positive Gibbs free energy.
Oxidation always occurs at the anode and reduction always occurs at the cathode, regardless of the type of cell. As mentioned previously, the charging battery requires energy input and behaves as an electrolytic cell. Exothermic reactions are characterized by a negative change in enthalpy. A reaction happening in an electrolytic cell is nonspontaneous. This means that the Gibbs free energy is always negative; however, other thermodynamic variables such as enthalpy and entropy can be either positive or negative.
Example Question #171 : Physical Chemistry
A charging battery is acting as a(n) __________ cell and a discharging battery is acting as a(n) __________ cell.
electrolytic . . . electrolytic
electrolytic . . . galvanic
galvanic . . . galvanic
galvanic . . . electrolytic
electrolytic . . . galvanic
A charging battery consumes energy from a power source like an electrical outlet, whereas a discharging battery releases energy and powers a device; therefore, a charging battery behaves as an electrolytic cell whereas a discharging battery behaves as a galvanic cell.
Example Question #174 : Physical Chemistry
Lithium batteries consist of lithium compounds and manganese dioxide. The reduction potential for lithium is 

I. Oxidation of manganese
II. Reduction of lithium
III. Oxidation of lithium
I only
II and III
I and II
III only
III only
A discharging battery behaves like a galvanic cell; therefore, it is characterized by a spontaneous reaction. This means that the reaction happening in a discharging battery has a positive standard reaction potential. Given the information in the question, we will get a positive standard reaction potential if the lithium atom is oxidized (half reaction potential = 


Example Question #1 : Other Electrochemistry Concepts

A 
First we need to convert minutes to seconds (10min=600s), and knowing that 
If we follow the units carefully, we see that all of the units cancel out to give us a value in grams of silver, which is what we are looking for.
Certified Tutor
All Physical Chemistry Resources