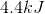All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : Physical Chemistry
What amount of heat must be added to a 20-gram sample of ice in order to raise the temperature from 

This question requires three steps:
1. We need to raise the temperature of the ice from 

2. We need to melt the ice.
3. We need to raise the temperature of the water from 

Steps one and three can use the equation:
Step 2 requires the enthalpy of fusion to be multiplied by the mass of the water sample.
Finding these three added heats will give us the total amount of heat needed to raise the temperature from 

Example Question #22 : Physical Chemistry
What is the process of converting a solid directly to a gas?
Condensation
Deposition
Sublimation
Freezing
Sublimation
Certain substances, such as carbon dioxide, are able to skip the liquid phase and go from a solid to a gas under standard conditions. This process is called sublimation.
Example Question #1 : Heat Capacity And Specific Heat
What is the specific heat capacity for a 50-gram sample of metal that increases in temperature by 10 degrees celsius when 2000 joules of energy is added?
Use the equation:
We can calculate the specific heat capacity for the unknown metal. Since we know the added heat 



Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry
A 

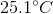


It is impossible to determine
Recall that the formula for specific heat is 
Remark: keep in mind that the release of energy and the cooling of the metal will give negative values for both 

Example Question #4 : Thermochemistry
The heat capacity of a bomb calorimeter assembly is 



A bomb calorimeter is a device used to measure the quantity of heat change for a process. The heat of a reaction which is denoted as 
The heat capacity of a calorimeter is:
Plugging the values given into the equation gives:
Using the relation provided earlier:
Because we are dealing with 1.1 grams of sucrose, the heat of combustion of sucrose is:
Example Question #5 : Thermochemistry
The heat capacity of a bomb calorimeter assembly is 



A bomb calorimeter is a device used to measure the quantity of heat change for a process. The heat of a reaction which is denoted as q, is the negative of the thermal energy gained by the calorimeter:
The heat capacity of a calorimeter is:
Plugging the values given into the equation gives:
Using the relation provided earlier:
Because we are dealing with 1.65 grams of sucrose, the heat of combustion of sucrose is:
Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry
Which of the following are endothermic?
Freezing
More than one of these are endothermic processes
Condensation
Melting
Melting
Endothermic processes involve a positive change in enthalpy. This means that the enthalpy of products is higher than the enthalpy of reactants and net heat energy is consumed. Phase changes that involve increasing the distance between particles (meaning conversion of solid to liquid (melting), liquid to gas (evaporation) and solid to gas (sublimation)) require an input of energy and are considered endothermic processes. On the other hand, phase changes that decrease the distance between particles (such as gas to liquid (condensation), liquid to solid (freezing), and gas to solid (deposition)) release energy and are considered exothermic processes.
Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry
Which of the following is true regarding an exothermic reaction?
I. Entropy always increases
II. It is always spontaneous
III. It can facilitate other energy-consuming reactions
III only
II only
I and III
I and II
III only
Exothermic reactions involve release of heat energy. This means that the energy of the products is lower than the energy of the reactants. Entropy is the measure of disorder in a system. It does not depend on the enthalpy and can increase or decrease during an exothermic process. Spontaneity is determined by looking at the change in Gibbs free energy, 



Example Question #2 : Thermochemistry
In an __________ reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants; in an __________ reaction the reactants are more stable than the products.
endergonic . . . endergonic
exergonic . . . exergonic
exergonic . . . endergonic
endergonic . . . exergonic
exergonic . . . endergonic
Exergonic reactions release energy; therefore, the energy of products is lower than that of the reactants. Endergonic reactions consume energy; therefore, the energy of products is greater than that of the reactants. In other words, exergonic reactions are spontaneous, while endergonic reactions are nonspontaneous, and require the net input of energy to drive the reaction.
Example Question #3 : Endothermic And Exothermic Reactions
Consider the following spontaneous reaction:
What can you conclude about the enthalpy change in this reaction?
Cannot be determined from the given information
It is positive
It is zero
It is negative
It is negative
We need to use the following equation to answer this question:
Above, 





Rearranging and solving the equation above for 
Since both 


All Physical Chemistry Resources