All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #8 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle , hypotenuse and . Using the definition of , find the length of leg . Round all calculations to the nearest tenth.
In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that , and we know that and hypotenuse . Therefore, a simple substitution and some algebra gives us our answer.
Use a calculator or reference to approximate cosine.
Isolate the variable term.
Thus, .
Example Question #9 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle , hypotenuse and . Using the definition of , find the length of leg . Round all calculations to the nearest tenth.
In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that , and we know that and hypotenuse . Therefore, a simple substitution and some algebra gives us our answer.
Use a calculator or reference to approximate cosine.
Isolate the variable term.
Thus, .
Example Question #10 : How To Find A Missing Side With Sine
In a given right triangle , hypotenuse and . Using the definition of , find the length of leg . Round all calculations to the nearest hundredth.
In right triangles, SOHCAHTOA tells us that , and we know that and hypotenuse . Therefore, a simple substitution and some algebra gives us our answer.
Isolate the variable term.
Thus, .
Example Question #81 : Trigonometry

What is the sine of ?
Sine can be found using the SOH CAH TOA method. For sine we do .
Example Question #82 : Trigonometry
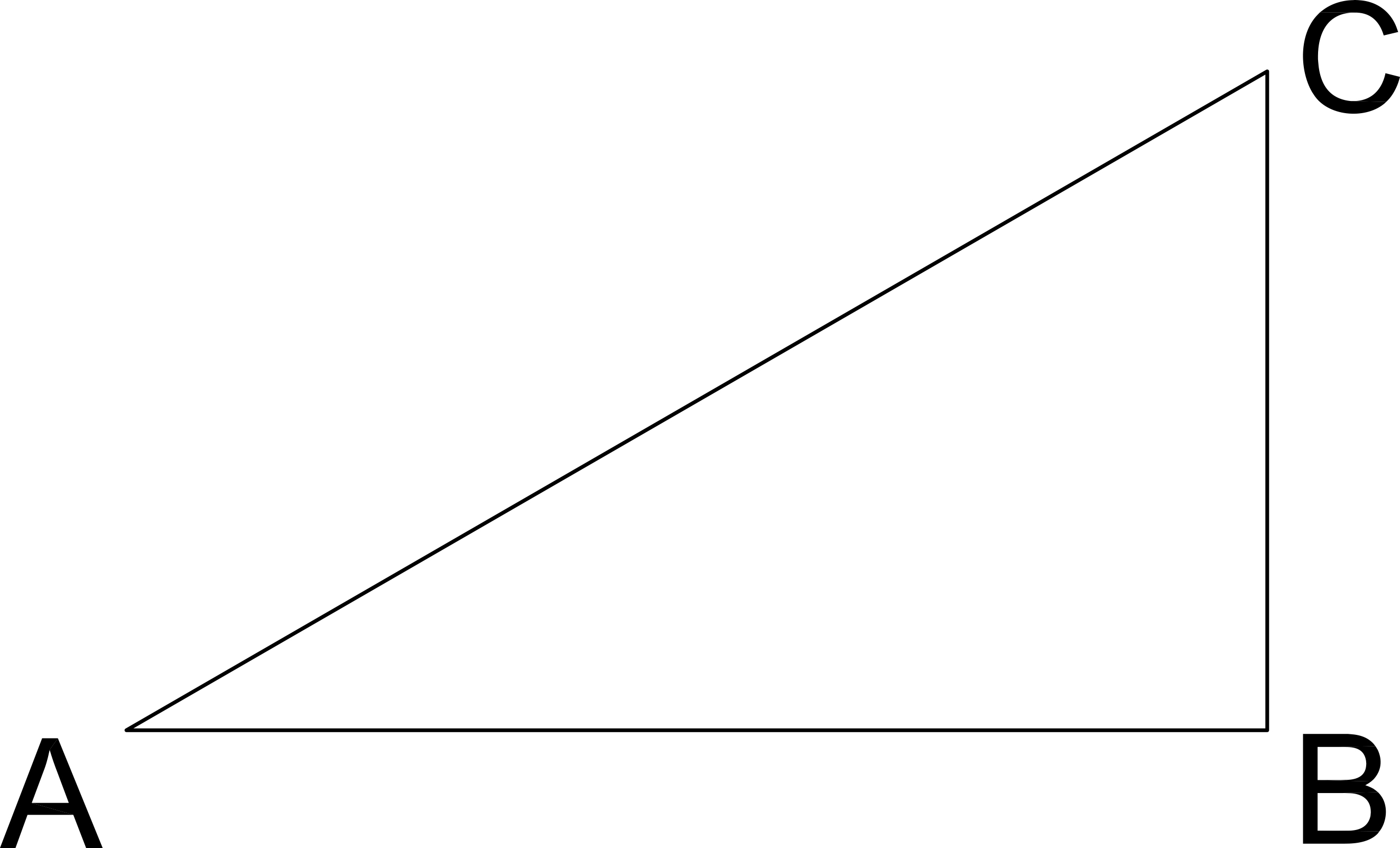
See right triangle ABC. If the length AB is 8 and the length of BC is 6, what is the sine of angle A?
0.8
6
10
0.6
1
0.6
Sine A = Opposite / Hypotenuse = BC / AC
To find AC, use Pythagorean Theorum
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
82 + 62 = AC2
64 + 36 = AC2
100 = AC2
AC = 10
Sine A = BC / AC = 6 / 10 = 0.6
Example Question #83 : Trigonometry
Solve for over the interval
Q = π or 2π
Q = π or does not exist 2
Q = π or 3π 2 2
Q = 3π or does not exist 2
Q = 3π or does not exist 2
Substitute x = sinQ and solve the new equation x2 + 3x = –2 by factoring. Be sure to change variables back to Q. As a result, sinQ = –1 or sinQ = –2. This function is bounded between –1 and 1 so sinQ can never be –2 and sinQ is –1 only at 3π/2 or 270 °.
Example Question #84 : Trigonometry
If , , and , what is the sine of ?
Recall that sin = opposite / hypotenuse. Based on the figure shown, we see that is the opposite side needed and is the hypotenuse. Plug these values in to solve.
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Sine Of An Angle

Triangle shown is a right triangle. If line and line , what is the sine of the angle at ?
Now solve for using Pythagorean Theorem:
Example Question #3003 : Act Math
If , and if is an angle between and degrees, which of the following equals ?
An angle between and degrees means that the angle is located in the second quadrant.
The tangent function is derived from taking the side opposite to the angle and dividing by the side adjacent to the angle (, as shown in the image).

Hence, the side is units long and side is units high. Therefore, according to Pythagorean Theorem rules, the side must be units long (since ).
The sine function is positive in the second quadrant. It is also equivalent to the side opposite the angle () divided by the hypotenuse ().
This makes .
Example Question #3004 : Act Math
A sine function has a period of , a -intercept of , an amplitude of and no phase shift. These describe which of these equations?
Looking at this form of a sine function:
We can draw the following conclusions:
- because the amplitude is specified as .
- because of the specified period of since .
- because the problem specifies there is no phase shift.
- because the -intercept of a sine function with no phase shift is .
Bearing these in mind, is the only function that fits all four of those.
All ACT Math Resources






































































































































