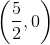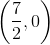All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #353 : Coordinate Geometry
Add 
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Example Question #354 : Coordinate Geometry
Multiply the complex conjugate of 

The complex conjugate of a complex number 




Example Question #355 : Coordinate Geometry
Multiply the complex conjugate of 8 by 
None of the other responses gives the correct product.
The complex conjugate of a complex number 




Example Question #356 : Coordinate Geometry
Multiply the complex conjugate of 

None of the other responses gives the correct product.
The complex conjugate of a complex number 



Multiply this by 
Recall that by definition 
Example Question #411 : Geometry
Multiply the following complex numbers:
FOIL the product out:
To FOIL multiply the first terms from each binomial together, multiply the outer terms of both terms together, multiply the inner terms from both binomials together, and finally multiply the last terms from each binomial together.
Recall that i is an imaginary number and by definition 
Example Question #1 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the equation of the vertical asymptote of the graph of the equation 
The vertical asymptote of an inverse variation function is the vertical line of the equation 





Example Question #1 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the 

The graph has no 
The graph has no 
The 




This is identically false, so the graph has no 
Example Question #2 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the 

The graph has no 
The 






Example Question #4 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the slope of the line that passes through the 


The line cannot exist as described.
The line cannot exist as described.
The graph of 


and
This is identically false, so the graph has no 
Example Question #1 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the 



The graphs of the equations do not intersect.
The graphs of the equations do not intersect.
Substitute 

The discriminant of this quadratic expression is 


The discriminant being negative, there are no real solutions to this quadratic equation. Consequently, there are no points of intersection of the graphs of the two equations on the coordinate plane.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources