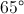All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
Find the perimeter of a triangle with side lengths of 
To find the perimeter of a triangle, add up all of its sides.
Example Question #541 : Geometry
Find the perimeter of the triangle below:

First, find the length of the missing side.
Since the angle measurements in the base of the triangle are the same, this is an isosceles triangle. The side lengths directly across from the equal angles must be the same. Thus, the missing side length is 
Now, to find the perimeter, add up all the side lengths.
Example Question #542 : Geometry
Find the perimeter of the triangle below:

First, find the length of the missing side.
Since the angle measurements in the base of the triangle are the same, this is an isosceles triangle. The side lengths directly across from the equal angles must be the same. Thus, the missing side length is 
Now, to find the perimeter, add up all the side lengths.
Example Question #543 : Geometry
Find the perimeter of the triangle below:

First, find the length of the missing side.
Since there are two angles that are the same, this is an isosceles triangle. The side lengths directly across from the equal angles must be the same. Thus, the missing side length is 
Now, to find the perimeter, add up all the side lengths.
Example Question #544 : Geometry
Find the perimeter of the triangle below:

First, find the length of the missing side.
Since there are two angles that are the same, this is an isosceles triangle. The side lengths directly across from the equal angles must be the same. Thus, the missing side length is 
Now, to find the perimeter, add up all the side lengths.
Example Question #545 : Geometry

Figure NOT drawn to scale.
If 


The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so
Example Question #1 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
If the vertex angle of an isoceles triangle is 
In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are the same. Also, the three angles of a triangle add up to 
So, subtract the vertex angle from 

Because there are two base angles you divide 


Example Question #546 : Geometry

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
Refer to the above diagram.
Which of the following could be a measure of 
All of the other choices give a possible measure of 
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so

We also have the following constraints:
Then, by the addition property of inequalities,
Therefore, the measure of 

Example Question #12 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles

Refer to the above diagram.
Which of the following could be a measure of 
All of the other responses are correct.
All of the other responses are correct.
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is the sum of the measures of its remote interior angles, so
or
Therefore, the maximum value of 


The minimum value of 


Therefore,
Since all of the choices fall in this range, all are possible measures of 
Example Question #1 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
Find the angle measurement of 

All the angles in a triangle must add up to 
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources