All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #101 : Physical Chemistry
In an atom or molecule, why can't two electrons have the same four electronic quantum numbers?
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
Harmonic Reaction Orders
The first law of thermodynamics
Kinetic energy operator
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle explains various phenomena such as the structure of atoms and how different atoms combine to share electrons. When you have two electrons that are located in the same orbital, the quantum numbers n, l and ml are the same. However, ms will be different. Two electrons cannot have the same four electronic quantum numbers because no more than two electrons may occupy an orbital, and if they do, the spin of one must cancel the spin of the other so their spins will have a zero net spin angular momentum.
Example Question #41 : Nuclear, Quantum, And Molecular Chemistry
What is the hybridization on the nitrogen atom in a molecule of ammonia?
sp2
sp3d
sp
sp3
sp3
The hybridization of an atom can be determined by the number of atoms it is bonded to, as well as the number of lone pairs it has. Two of these variables would be sp, three variables would be sp2, and four would be sp3.
The nitrogen in ammonia is bonded to three atoms of hydrogen, but also has a lone pair in order to satisfy its octet. This means that nitrogen exhibits sp3 hybridization.
Example Question #4 : Atoms And Elements
Which of the following are true regarding 

I. Both 

II. In a given shell, 
III. 

III only
I only
I and III
I and II
I and III
Orbitals are regions in an electron shell where electrons might be located. There are several types of orbitals such as 










Example Question #2 : Orbitals And Hybridization
What is true when comparing the electron configuration of elemental sodium 

Elemental sodium is paramagnetic
The sodium ion has one additional electron in an 
The outermost shell of the sodium ion has one electron
The sodium ion has more electrons in 
Elemental sodium is paramagnetic
To answer this question, we need to find the electron configuration of both elemental sodium and sodium cation. If we look at the periodic table we can see that sodium is found on the first column. Since it is found in the first column, sodium has one valence electron. To complete octet, sodium will readily lose an electron and become a positively charged sodium ion. The electron configuration for sodium is 






Example Question #11 : Atoms And Elements
It is observed that a molecule has three hybridized orbitals in its outermost shell. What can you conclude about this molecule?
It has a lone pair electron
It has four single bonds
It has a double bond
None of these
It has a double bond
Hybridization is a process involving the fusion, or hybridization, of 














































Example Question #3 : Orbitals And Hybridization
Which of the following is true regarding carbon tetrachloride?
Hybridization in this molecule involves three times as many 

The carbon in this molecule has similar hybridization as the carbon in carbon dioxide
Hybridization in this molecule involves two times as many 

More than one of these are true
Hybridization in this molecule involves three times as many 

Carbon tetrachloride, 














Example Question #101 : Physical Chemistry
How many valence electrons are in an atom of phosphorus?
Five
Eight
Three
Thirteen
Five
When determining the number of valence electrons for an atom, simply count the number of electrons present in the outermost shell's s and p orbitals. Phosphorus has two electrons in the 3s subshell, and three more in the 3p subshell, making a total of five valence electrons.
Example Question #1 : Valence Electrons
What is the complete electron configuration for the sulfur atom?
1s22s22p63s23p2
1s22s22p63s23p2
1s42p63s23p4
1s42p63s23p4
1s22s22p63s23p4
1s22s22p63s23p4
The types of subshells, from smallest to largest, are as follows: s, p, d, and f. These four subshells correspond respectively to the following quantum numbers: 0, 1, 2, and 3. From the periodic table, it is known that sulfur has 16 electrons. Additionally, the maximum number of electrons the s sublevel can hold is 2. The maximum number of electrons that the p subshell can hold is 6, and electrons fill orbitals from lowest to highest energy. 1s22s22p63s23p4 is the only choice that meets the criteria.
Example Question #1 : Valence Electrons
Arrange the following ions in order of decreasing ionic radius: nitride ion, oxide ion, sodium ion, aluminum ion.
The ions have the same ionic radius.
Notice that all the ions have the same electron configuration as neon: 1s22s22p6. Substances with the same number of electrons and the same electron configuration are isoelectronic, meaning the number of electrons is the same but the number of protons is not. In an isoelectronic series, the ion with the most protons is smallest because the nucleus exerts a stronger force of attraction and the electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. Consequently, the ion with the fewest protons is largest. 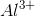
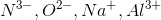
Example Question #12 : Atoms And Elements
Which of the following trends decreases as you move from left to right on the periodic table?
Atomic radius
Electron affinity
Ionization energy
Electronegativity
Atomic radius
Although it may seem counterintuitive, atomic radius does decrease from left to right on the periodic table. The reason for this is because the added positive charge in the nucleus causes the elctrons to be pulled more strongly towards the center, which decreases the atomic radius.
All Physical Chemistry Resources








