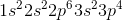All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #91 : Physical Chemistry
Which of the following molecules has the smallest bond angle?
Carbon dioxide
Ammonia
Methane
Water
Water
One of the biggest factors that can affect the bond angles in a molecule is the presence of lone pairs. A general rule is that each lone pair will decrease the predicted bond angle by about two degrees. Methane, for example, has no lone pairs on the central carbon, so its bond angles are 109.5 degrees. Ammonia, however, has one lone pair, which makes its angles closer to 107.5 degrees. Finally, water has 2 lone pairs, giving it a bond angle of about 105 degrees.
Example Question #3 : Molecules
Which molecule exhibits trigonal pyramidal geometry?
Carbon dioxide
Ammonia
Boron trifluoride
Methane
Ammonia
A trigonal pyramidal geometry is witnessed when molecules have a central atom bonding to three additional atoms and one lone pair. The nitrogen atom in ammonia has three hydrogens attached, as well as a lone pair, in order to satisfy its octet. This gives ammonia a trigonal pyramidal geometry.
Methane has a tetrahedral geometry, carbon dioxide is linear, and boron trifluoride is trigonal planar.
Example Question #91 : Physical Chemistry
A metal with sp3d2 hybridized orbitals contains eight valence electrons. If four monodentate ligands are bound to this metal, what is the resulting molecular geometry?
square planar
tetrahedral
T-shaped
seesaw
square pyramidal
square planar
An sp3d2 hybridized atom contains six degenerate orbitals. Hund's Rule states that all degenerate orbitals must be singly occupied before any orbital becomes doubly occupied. This molecule contains eight valence electrons, which results in two doubly occupied hybrid orbitals (two lone pairs) and four singly occupied hybrid orbitals to which the ligands bind. Thus, the molecule contains four bonds and two lone pairs, which corresponds to a square planar geometry.
Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
How many neutrons are present in the nucleus of one atom of 
From the periodic table, we find that the atomic number, i.e., the number of protons in the nucleus of 


Example Question #2 : Atoms And Elements
Which atomic symbol represents a period five transition metal that has 42 electrons when it forms a 
Transition metals extend from groups 3 through 12 and periods 4 through 7. Ru, in its neutral state, has 44 electrons. Therefore, when it becomes a 
Example Question #3 : Atoms And Elements
What is the mass number, atomic number, and charge, of the isotope of an atom that contains 34 protons, 36 neutrons, and 36 electrons?
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
Mass number:
Atomic number:
Charge:
The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the element, so from the periodic table, we find that the element with atomic number 34 is selenium. Since 

Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
Which of the following organizes the forces from strongest to weakest?
Van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding
Dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding, van der Waals forces
Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding, dipole-dipole interactions
Hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, van der Waals forces
Covalent bonding, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, van der Waals forces
Covalent bonding, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, van der Waals forces
Covalent bonds are by far the strongest, requiring 
Next are hydrogen bonds, which require between 
Next are dipole-dipole interactions, which require 
Finally, van der Waals forces are the weakest of those listed, requiring 
Example Question #4 : Atoms And Elements
Which of the following electron configurations indicates an atom in an excited state?
An atom is considered to be in an excited state when one of the electrons has jumped to a higher energy level while a lower energy level is available. In the case of 
Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
What is the complete ground state electron configuration for the magnesium atom?
1s22s22p23s2
1s22s22p63s6
1s22s22p63s2
1s42p63s2
1s22s23s2
1s22s22p63s2
Magnesium has an atomic number of 12, so the total number of electrons in its configuration should add up to twelve. The maximum number of electrons in the s subshell is two. Of all the answer choices, only 1s22s22p63s2 fits the criteria. The sum of the exponent values is 12, matching the atomic number of magnesium, and the number of electrons in the s and p subshells matches the maximum amount possible.
Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
What is the complete ground state electron configuration for the iron atom?
1s22s22p63s24s23d6
1s42s22p63s23p24s23d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6
1s22s22p63s23p63d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6
Iron has an atomic number of 26, so the total number of electrons in its configuration should add up to twenty six. The maximum number of electrons in the s subshell is two. The sum of the exponent values is 26, matching the atomic number of magnesium, and the number of electrons in the s and p subshells matches the maximum amount possible.
Certified Tutor
All Physical Chemistry Resources