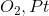All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #13 : Organic Oxidizing Agents
Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent, 

Example Question #461 : Organic Chemistry
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 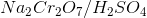
An aldehyde
A carboxylic acid
A primary alcohol
A secondary alcohol
A secondary alcohol

Not only can 
Example Question #2 : Using Dichromate Compounds

What would be the product of the given reaction?


![]()
![]()

The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by 

Example Question #462 : Organic Chemistry
Which of the following reagents can turn primary alcohols into a carboxylic acid?
Jones Reagent (chromic acid in acetone)
PCC
Tollen's test
Jones Reagent (chromic acid in acetone)
The Jones reagent can convert primary alcohol to acids and secondary alcohols to ketones. The Tollen's test only converts aldehydes to carboxylic acids. PCC can only convert primary and secondary alcohol to aldehydes and ketones, respectively. 

Example Question #463 : Organic Chemistry
What is an appropriate reagent to convert a primary alcohol to an aldehyde?
To form the aldehyde, the alcohol must be oxidized. However, potassium permanganate and chromic acid are too strong and would yield a carboxylic acid. Ozonolysis works with alkenes and oxygen over platinum would not react. PCC is correct because it will oxidize the alcohol to form an aldehyde but is too weak to continue on to form the carboxylic acid.
Example Question #1 : Organic Reducing Agents
As a reducing agent, 
hydrogen atom
hydride ion
hydrogen molecule
proton
electron
hydride ion
Sodium borohydride donates a hydride ion to a ketone or aldehyde. In order to form a ketone or aldehyde, a nucleophile must attack the carbonyl group. This is because the ketone or aldehyde has an electrophilic carbon—a nucleophile must attack it in order for any reaction to occur. A hydride ion is the only answer choice that plays the role of a nucleophile.
Example Question #1 : Using Sodium Borohydride
Which of the following reaction conditions will selectively reduce the ketone in the following compound, retaining the alkene functionality?

Pd, BaSO4, and H2 in hexanes
Pd and H2 in hexanes
LiAlH4 in THF
NaBH4 in MeOH
CeCl3 and NaBH4 in MeOH
CeCl3 and NaBH4 in MeOH
The correct choice, CeCl3 and NaBH4 in MeOH, shows reagents know as "Luche conditions," which are able to modify the reactivity of sodium borohydride to reduce the carbonyl to an alcohol without affecting alkene groups. This occurs as the cerium ion coordinates strongly to the carbonyl oxygen, which subsequently greatly enhances the electrophilicity at the carbonyl carbon. Nucleophilic attack of the hydride readily occurs, simultaneously destroying the electropilicty of the beta carbon of the alkene, such that it will not be reduced by the hydride reagent.
The incorrect answer choices would give various undesired products as detailed below:
NaBH4 in MeOH
Use of unmodified sodium borohydride would result in a 1,4 conjugate addition reaction, saturating the alkene, with a subsequent reduction of the ketone to an alcohol.
LiAlH4 in THF
Use of lithium aluminum hydride would give the same product as use of unmodified sodium borohydride, following the same reduction mechanism.
Pd and H2 in hexanes
This reagent will give reduction of the alkene only.
Pd, BaSO4, and H2 in hexanes
This reagent combination, known as Lindlar's catalyst, will also reduce the alkene only. This reagent is typically used to selectively reduce an alkyne to an alkene.
Example Question #2 : Organic Reducing Agents
Which of these can be reduced by sodium borohydride?
None of these
2-butene
3-pentanone
2-butanol
Propanoic acid
3-pentanone
Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent with formula 
Example Question #1 : Organic Reducing Agents
Which of the following statements is false?



None of these
None of these
These are all true uses of 
Example Question #1 : Using Grignard Reagents
What is the product of the reaction between magnesium and any alkyl halide, in anhydrous ether?
An aldehyde
A Grignard reagent
An organolithium
An alkane
An alcohol
A Grignard reagent
The reaction between magnesium and an alkyl halide in anhydrous ether results in a Grignard reagent.
An organolithium would result from the same process, but the magnesium would need to be replaced by two equivalents of lithium. Alcohols are products of reactions between a Grignard reagent and a carbonyl.
All Organic Chemistry Resources