All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #251 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
A pharmaceutical company develops a drug that attacks lamins inside the nucleus. What can you conclude about this drug?
There is an increased trafficking of molecules between cytoplasm and nucleus
The prophase of mitosis cannot progress
It halts cholesterol synthesis
It increases the integrity of the chromosomes
The prophase of mitosis cannot progress
Lamins are intermediate filaments found inside the nucleus. Lamins attach to nuclear proteins and form a layer underneath the nuclear envelope (nuclear membrane) called the nuclear lamina. The nuclear lamina functions to position nuclear pores to let molecules pass between the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm. It also functions to break and resynthesize the nuclear envelope during mitosis. Recall that the nuclear envelope is broken down during the prophase of mitosis; therefore, lack of lamins will directly affect this phase of mitosis.
In addition to the aforementioned functions, lamins are also involved in maintaining the integrity of chromosomes. Lack of lamins will decrease the stability of chromosomes. Cholesterol and most other lipids are synthesized in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum; therefore, lamins are irrelevant to cholesterol synthesis. Since they are involved in positioning nuclear pores, lamins are important for exchanging molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Lack of lamins will decrease this trafficking.
Example Question #252 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
Which of the following processes occurs only in the nucleus?
I. Transcription
II. DNA replication
III. Translation
II only
I and II
III only
II and III
I and II
The central dogma of molecular biology states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. The first step is the replication of the genetic material, DNA, during the S phase of the cell cycle. The second step is the conversion of DNA to RNA. This process is called transcription and involves several enzymes that convert the DNA to mRNA. The final step is called translation, which involves the conversion of mRNA to protein.
DNA replication and transcription occur inside the nucleus because the enzymes required to carry out these processes are found in the nucleoplasm. Translation, on the other hand, occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Example Question #253 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
After performing a genetic study, a physician finds that a patient has a defect in the genetic material that codes for ribosomes. Where in the cell is this genetic material found?
Nucleolus
Periplasm
Histones
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
Genetic information that codes for ribosomes is found on the nucleolus. Recall that the nucleolus is a specialized structure found inside the nucleus that functions to assemble ribosomes from proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The DNA that encodes for rRNA is on the nucleolus or in the vicinity of the nucleolus.
The periplasm is the space between the inner and outer cell membrane in gram-negative bacteria; it is irrelevant to this question. The nuclear envelope is the phospholipid bilayer that covers the nucleus. It does not contain any genetic information. Histones are proteins that organize and structure DNA strands; they don’t have any genetic information.
Example Question #251 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
Which of the following is true of the RNA transcripts in the nucleolus and nucleus?
None of these are true
Translation of nuclear transcripts occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas translation of nucleolar transcripts occurs in nucleoplasm
Translation of both transcripts occurs in the cytoplasm
Translation of nuclear transcripts occurs in the nucleoplasm, whereas translation of nucleolar transcripts occurs in the cytoplasm
None of these are true
In the nucleolus, the transcripts synthesized are rRNA molecules. The unique aspect of rRNA molecules is that they are never converted to proteins; therefore, they never undergo translation. The rRNA molecules synthesized by the nucleolus are assembled with other proteins to create ribosomes; they themselves never undergo translation.
Transcription in the rest of the nucleus produces mRNA molecules that enter the cytoplasm and undergo translation to create proteins.
Example Question #252 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
The nucleolus is responsible for synthesis of which of the following compounds?
None of these
DNA
Arachidonic acid
rRNA
tRNA
rRNA
The nucleolus has genes for transcribing ribosomal RNA. RNA polymerase I in the nucleolus transcribes the gene for ribosomal RNA and causes formation of ribosomal complexes. mRNA and tRNA are transcribed elsewhere in the nucleus and use RNA polymerase II and III, respectively. Arachidonic acid is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid, which plays roles in cell-signaling, prostaglandin synthesis, and the immune response, and is synthesized in the cytosol.
Example Question #91 : Cellular Structures And Organelles
Where is the eukaryotic electron transport chain located?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Nuclear envelope
Mitochondrial matrix
Plasma membrane
Intermembrane space
Inner mitochondrial membrane
The electron transport chain (ETC) is located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is composed of a set of cytochromes which function in creating a proton (H+) gradient which provides the energy for ATP synthase to make ATP.
Note that the prokaryotic electron transport chain occurs on the plasma membrane with a proton gradient generated between two outer membranes or between the membrane and cell wall.
Example Question #1 : Mitochondria And Chloroplasts
Which of the following do not contain mitochondria?
Muscle cells
Fungal cells
Bird cells
Red blood cells
Worm cells
Red blood cells
Red blood cells, although they are eukaryotic cells, do not contain mitochondria. This is because red blood cells function in transporting oxygen. Mitochondria, on the other hand, require oxygen in order to make ATP. If red blood cell had mitochondria, they would use up the oxygen that the cells are trying to transport.
Example Question #101 : Cellular Structures And Organelles
Which of the following statements about mitochondria could be used as support for the endosymbiotic theory?
Cells that are involved in movement, such as muscle cells and the flagella of sperm, tend to contain comparatively large numbers of mitochondria
A proton gradient along the inner mitochondrial membrane powers the aerobic production of ATP
Plant cells contain both mitochondria and chloroplasts
Like prokaryotes, a mitochondrion has a single circular chromosome
Mitochondria help regulate apoptosis, which is the controlled death of aged or injured cells
Like prokaryotes, a mitochondrion has a single circular chromosome
Though all of the answer choices are correct statements, only one provides support for the endosymbiotic theory. This commonly supported theory proposes that mitochondria arose as single-celled prokaryotes that were engulfed by larger cells. These cells developed a symbiotic relationship that eventually led to current eukaryotic cells. So, for a statement to support this theory, it must make a connection between mitochondria and the prokaryotes from which they arose—such as the fact that they have similar DNA structures.
Example Question #3 : Mitochondria And Chloroplasts
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
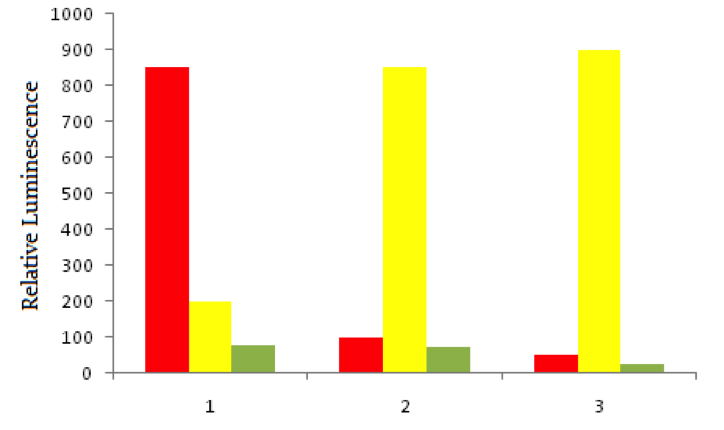
You are using a PET scan to ascertain the spread of bladder cancer in a patient. PET scans use metabolic activity by mitochondria to focus on areas of increased metabolism, consistent with cancer cell activity. Which of the following is NOT true of mitochondria?
They have cristae on their inner membranes
They have their own genome
They house the Kreb's cycle
Most of their ATP is produced via substrate-level phosphorylation
They have inner and outer membranes
Most of their ATP is produced via substrate-level phosphorylation
Mitochondria have all of the above qualities, except most of their ATP is produced via oxidative phosphorylation.
Example Question #4 : Mitochondria And Chloroplasts
Most scientists subscribe to the theory of endosymbiosis to explain the presence of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. According to the theory of endosymbiosis, early pre-eukaryotic cells phagocytosed free living prokaryotes, but failed to digest them. As a result, these prokaryotes remained in residence in the pre-eukaryotes, and continued to generate energy. The host cells were able to use this energy to gain a selective advantage over their competitors, and eventually the energy-producing prokaryotes became mitochondria.
In many ways, mitochondria are different from other cellular organelles, and these differences puzzled scientists for many years. The theory of endosymbiosis concisely explains a number of these observations about mitochondria. Perhaps most of all, the theory explains why aerobic metabolism is entirely limited to this one organelle, while other kinds of metabolism are more distributed in the cellular cytosol.
A scientist is presenting her evidence in support of the theory of endosymbiosis. Which of the following assertions is FALSE?
Mitochondria have a double membrane
Mitochondia have their own ribosomes
Mitochondria undergo a process similar to binary fission
Mitochondria have a reduced genome
Mitochondria have the full genetic complement of prokaryotes
Mitochondria have the full genetic complement of prokaryotes
Mitochondria do not have the full prokaryotic genetic complement. Over the eons since they were originally free living, most of their genes have been transferred to their host cells, reducing the mitochondrial genome.
All other statements are true.
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




