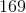All ISEE Middle Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #32 : Probability

The six faces of a die are shown in the fold-out diagram above; this die and an identical one are tossed.
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The probability that the dice land with sides of the same color facing upward
(b) The probability that the dice land with sides of different colors facing upward
(a) is the greater quantity
(b) is the greater quantity
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) and (b) are equal
As seen from the table below, out of the thirty-six equally probable rolls, eighteen result in the same color facing upward on both dice (indicated by an "S"); eighteen result in different colors facing upward (indicated by a "D").

The events occur with the same frequency, so they also occur with the same probability.
Example Question #33 : Probability

The six faces of a fair die are shown in the fold-out diagram above; this die and an identical one are tossed.
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The probability that the sum of the numbers facing upward is even
(b) The probability that the sum of the numbers facing upward is odd
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) is the greater quantity
As seen from the table below, out of the thirty-six equally probable rolls, twenty result in an even sum (these are set apart with red squares), and sixteen result in an odd sum.

Since even sums happen with greater frequency, the probability of an even sum is greater.
Example Question #38 : Outcomes

The above diagram shows a set of balls. The odd-numbered balls are placed in Box A; the even-numbered balls, in Box B. Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The probability that a ball randomly drawn from Box A will be white.
(b) The probability that a ball randomly drawn from Box B will be white.
(a) is the greater quantity
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is the greater quantity
The diagram below shows how the balls are separated. 
Box A contains 13 balls, of which 4 are white; the probability of a random draw from this box resulting in the draw of a white ball is 
Box B contains 12 balls, of which 6 are white; the probability of a random draw from this box resulting in the draw of a white ball is 
Rewriting the probabilities in terms of a common denominator:


Example Question #39 : Outcomes
Two fair six-sided dice are thrown. What is the probability that the product is greater than or equal to
The rolls that yield a product greater than or equal to 20 are:
These are 8 out of 36 rolls, so the probability of getting one of them is
Example Question #1 : Data Analysis

Define:
Universal set 






If all of the natural numbers were to be placed in their appropriate places in the above Venn diagram, which of the following would be placed in the gray region?
The gray region is the region outside both 

1,565 and 3,890 can be eliminated as choices as each is divisible by 5: the former ends in 5 and the latter ends in 0.
7,431 and 3,966 can be eliminated as each is divisible by 3: 

7,916 is not divisible by 5 as it ends in 6; it is not divisible by 3 as 
Example Question #2 : Data Analysis

Define:
Universal set 






If all of the natural numbers were to be placed in their appropriate places in the above Venn diagram, which of the following would be placed in the gray region?
The gray region is the region outside both 

1,565 and 3,890 can be eliminated as choices as each is divisible by 5: the former ends in 5 and the latter ends in 0.
7,431 and 3,966 can be eliminated as each is divisible by 3: 

7,916 is not divisible by 5 as it ends in 6; it is not divisible by 3 as 
Example Question #1 : Data Analysis
Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The midrange of the data set
(B) The midrange of the data set
(A) and (B) are equal
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
The midrange of a data set is the mean of its least and greatest elements. The midrange of the first data set is 

Example Question #2 : Data Analysis
Set 
Set 

What is the range of values in set 
To find the range of a set of numbers, you do not even have to put them in order. You merely need to subtract the smallest value from the largest. Given the way of constructing set 



Smallest: 
Largest:
Therefore, the range is:
Example Question #1 : How To Find Range
The members of set 
For values of 


What is the range of set 
To find the range of a set of numbers, you do not even have to put them in order. You merely need to subtract the smallest value from the largest. Given the way that we construct set 


Smallest: 
Largest:
Therefore, the range is:
Example Question #2 : Data Analysis
Set 
The members of set 



So, for instance, set T contains 

What is the range of set 
We first need to determine the members of set 

Our largest value is 

Certified Tutor
All ISEE Middle Level Quantitative Resources