All HiSET: Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #32 : Measurement And Geometry
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle whose legs are the following lengths:
The hypotenuse of a right triangle can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem. This theorem states that if we know the lengths of the two other legs of the triangle, then we can calculate the hypotenuse. It is written in the following way:
In this formula the legs are noted by the variables, 


Substitute and solve for the hypotenuse.
Simplify.
Take the square root of both sides of the equation.
Example Question #91 : Hi Set: High School Equivalency Test: Math
If the two legs of a right triangle are 






Step 1: Recall the Pythagorean theorem statement and formula.
Statement: For any right triangle, the sums of the squares of the shorter sides is equal to the square of the longest side.
Formula: In a right triangle 


Step 2: Plug in the values given to us in the problem....
Evaluate:
Simplify:
Simplify:
Take the square root...
Step 3: Simplify the root...
The length of the hypotenuse in most simplified form is 
Example Question #3 : Understand Right Triangles
Which of the following could be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle?
In each choice, the two shortest sides of the triangle are 9 and 12, so the third side can be found by applying the Pythagorean Theorem. Set 

Take the square root:

The correct choice is

Example Question #131 : Measurement And Geometry
Two of a triangle's interior angles measure 


A triangle that has interior angles of 



Since we know this triangle is a 30-60-90 triangle, we can use the special ratios that always hold true for this triangle's sides and angles to figure out the lengths of its other sides. The following ratio holds true for all 30-60-90 triangles, where the side in a fraction with a given angle is the side opposite that angle.
We're told that the hypotenuse of our triangle has a length of 




As you can see, for this particular triangle, 








Thus, the correct answer is 
Example Question #4 : Understand Right Triangles
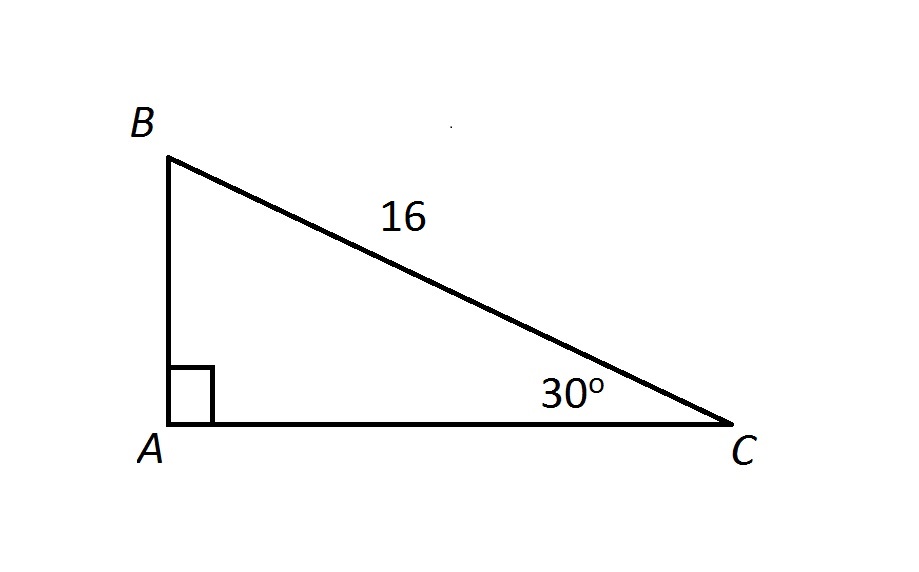
Examine the above triangle. Which of the following correctly gives the area of 
None of the other choices gives the correct response.
Since 



making 
By the 30-60-90 Triangle Theorem,

and
Refer to the diagram below:
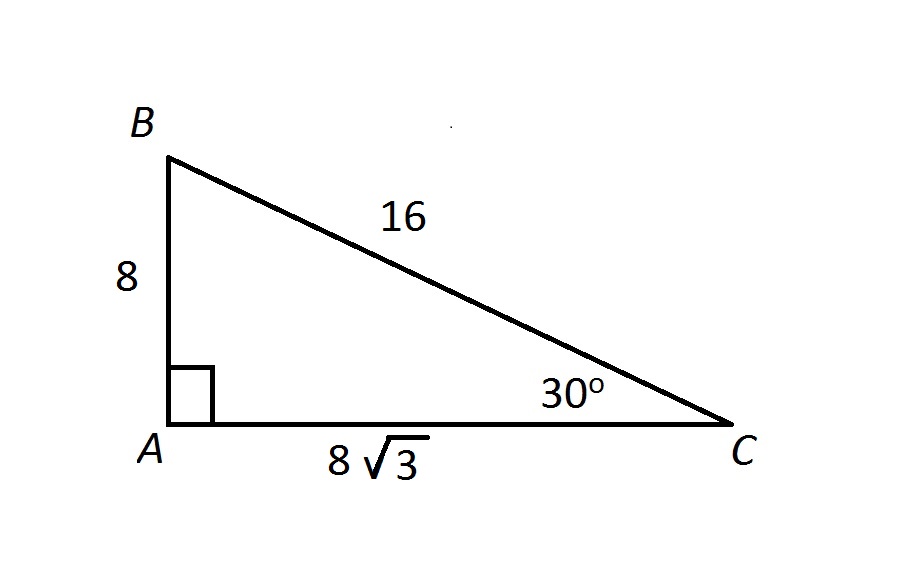
The area of a right triangle is equal to half the product of the lengths of its legs, so

the correct response.
Example Question #281 : Hi Set: High School Equivalency Test: Math
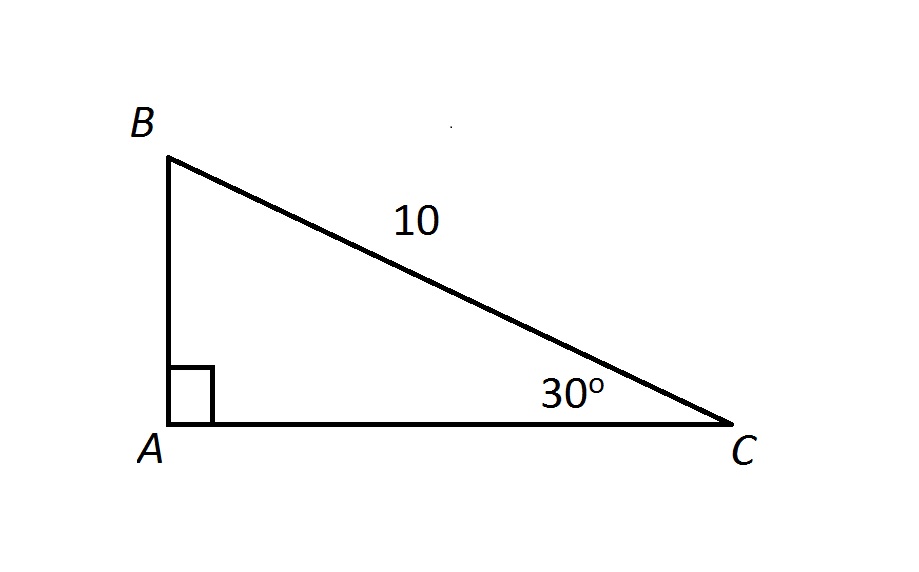
Examine the above triangle. Which of the following correctly gives the perimeter of 
Since 



making 
By the 30-60-90 Triangle Theorem,

and
Refer to the diagram below:
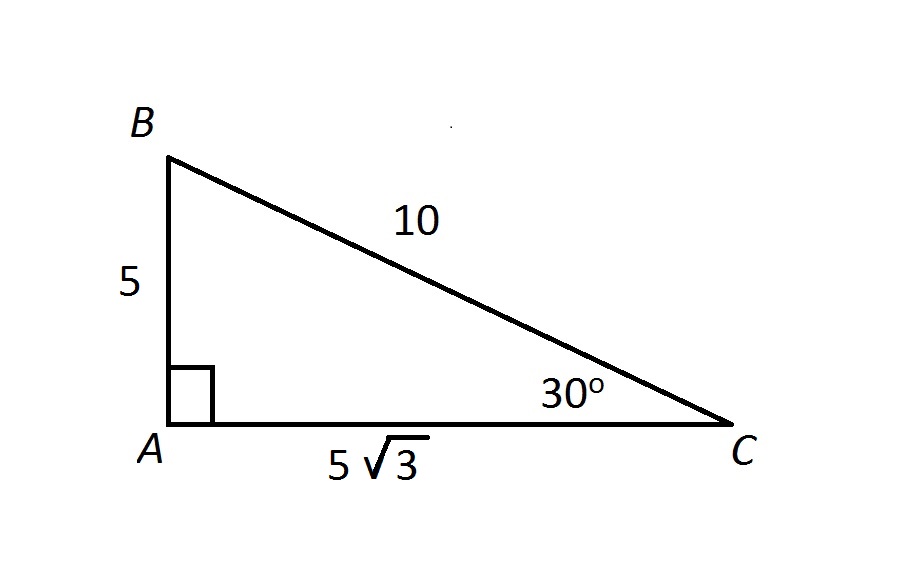
The perimeter - the sum of the sidelengths - is

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All HiSET: Math Resources





















































