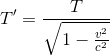All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #111 : Newtonian Mechanics And Motion
A cannon fires a cannon ball at an angle of 

How far will the ball be from the cannon once it hits the ground?
We must first determine the amount of time that the ball is in the air, then use the horizontal velocity to solve for the distance travelled.
In order to solve for the amount of time, we need to know the vertical initial velocity of the cannonball. This is given by the equation 

Knowing this, we can solve the amount of time it will take for the cannon ball to reach its maximum peak, with a velocity of 
This is the amount of time it takes for the ball to reach its peak, not the total time it is in the air. Since the ball must drop from the maximum height, we double the time and find that total flight time is 20.8s.
The next step is determining the horizontal initial velocity from the cannon. This is determined using the equation below.
Since we assume that there is no air resistance, we can conclude that the horizontal velocity of the cannonball will remain constant throughout its flight. As a result, the total displacement equation is simplified to the following: 
Example Question #381 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Using Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation equation, which of the following expressions is equal to the local gravitational acceleration 
On earth, 
The law of universal gravitation is equal to 
We can set these equations equal to one another and isolate 

Using the mass of the Earth, the radius of the Earth, and the gravitational constant, 


Example Question #11 : Submersion
An irregular solid has a mass of 

The difference between the mass as measured in air and the mass as measured when it is suspended in water is the mass of the displaced water, easily reduced to the volume of the solid.
First calculate the weight of the solid in air.
In water, it weighs 
Recall that buoyant force is equal to the weight of water displaced by the object.
Example Question #1 : Astrophysics
If the temperature of a blackbody doubles, what occurs to the wavelength of maximum emission?
It quadruples.
It is quartered.
It is halved.
No change.
It doubles.
It is halved.
This is an application of Wein's Law that states the following:





Example Question #12 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
By what factor will the energy emitted each second off the surface of a blackbody change if the the temperature of the object is tripled?
Stefan-Boltzmann's equation for a blackbody states:




Example Question #2 : Astrophysics
Using the kinetic theory of gas, what is the fundamental property of a planet that dictates if it is able to retain an atmosphere?
Number of moons
Magnetic field strength
Mass
Energy
Temperature
Mass
The kinetic theory of gas states:


Example Question #11 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
The difference in age for the twins in the Twin Paradox occurs during which key moment in the trip?
During the period of great acceleration during the changing of directions and return to Earth.
None of these
While approaching a black hole in space during the trip.
During the beginning of the journey traveling fast.
During the time returning to Earth traveling fast.
During the period of great acceleration during the changing of directions and return to Earth.
While moving clocks do in fact record time moving at different rates, the time dilation works both ways. This means that a stationary person will view a moving clock ticking slower, but at the same time, a person moving alongside the moving clock will see the stationary clock ticking slower. However, clocks experiencing great accelerations will be permanently changed, "losing" time relative to a clock not being accelerated. Thus, the age difference occurs during the portion of the journey when the traveler accelerates at a great rate in order to return to Earth.
Example Question #15 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A black hole is an object whose gravitational field is so strong that even light cannot escape. Assuming no change in radius, approximately how much mass would our Sun have to have in order to become a black hole?
Sun's radius:
To derive the Schwarzschild radius of a black hole, set gravitational potential energy equal to kinetic energy at escape velocity:
Solving for mass of the black hole:
Example Question #2 : Special Relativity
At one point in time, two twins are 30 years old. At this time, one of them gets on a rocket and travels at 0.8 c, for what he experiences to be 12 years. How old is the twin that remained on Earth when the traveling twin returns home?
42 years old
50 years old
70 years old
37 years old
50 years old
The equation for time dilation is given by:
In this problem v=0.8c T=12. Using this equation, we get:
Adding 20 years to the age initial age of 30:
The Earth-twin is now 50.
Example Question #17 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A meter stick, at an angle of 30 degrees with the x-axis, is traveling at 0.6c in the direction of the positive y-axis. To a stationary observer, how long does the meter stick appear to be?


Length contraction only occurs in the direction of motion. This means that the x component of the length, which is cos(30), does not change; length contraction only occurs the the y component, which is sin(30).
First, we find the Lorentz factor:
Next, we apply the time dilation equation to the length in the y direction:
Finally, we find the total length by combining the length-contracted y component and the unchanged x component:
All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources