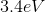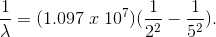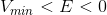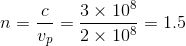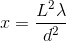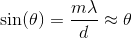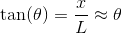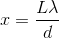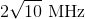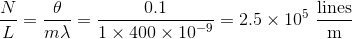All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #31 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
What wavelength will result in the most accurate measurement of the momentum of an electron?
Red light
Gamma-ray
Infrared
Radio
X-ray
Radio
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that:

Example Question #32 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
If a ground state particle is in a one-dimension square well, where is the probability of finding the particle equal to zero?

At the boundary.
In the middle.
None of these

At the boundary.
This is a fundamental concept question. For a ground state particle, the only place where the probability is equal to zero is at the boundary because the particle cannot be found there. He has to be in the box (not unlike a cat).
Example Question #1 : Atomic Spectra
What is the energy of the photon emitted when a Hydrogen atom makes a transition from the 



However, since the question asked what is the energy of the photon, it is the absolute value of the energy calculated above because of conservation of energy. The photon carries away the energy lost by the atom.
Example Question #1 : Atomic Properties
What color will be emitted in the 

Red
Blue
Yellow
Violet
Green
Violet

Here, 




By inverting, 
Example Question #1 : Circular And Rotational Motion
What relation must be true between the minimum potential energy and the total energy of the satellite for the shape of its orbit to be circular?
For a gravitation potential, the total energy is:

When the energy equals the minimum potential energy, the satellite has just enough energy to maintain a circular orbit around the planet. When the potential energy is larger than the total energy, the satellite spirals in toward the planet. When the total energy is greater than zero, the satellite is deflected out into space.
Example Question #1 : Electromagnetics, Waves, And Optics
A particle traveling through glass (index of refraction 1.33) emits Cherenkov radiation. Which of the following is a possible speed of the particle?
Cherenkov radiation is emitted by a particle traveling faster than the phase velocity of light in that medium. Because 
This is the minimum velocity of a particle to be emitting Cherenkov radiation in glass. This eliminates all answers except 


Example Question #1 : Waves
A monochromatic beam of 

The phase velocity of light through a medium with refractive index 
Solving this for 

Example Question #2 : Waves
A double slit experiment is set up with the following parameters: two slits are a separated by a distance 




The condition for constructive interference with double slit diffraction is given by:
Where 
Solving for the angle and using the small angle approximation, we get;
The distance 
Again, with the help of the small angle approximation. Setting the two thetas equal to each other and solving for 
For the central band, 


Example Question #3 : Waves
Two waves with frequencies: 
The beat from two combined sound waves is:
Example Question #1 : Diffraction
A beam of light, with wavelength 

The equation describing maxima of a diffraction grating is:
Where d is the separation of slits, which can also be expressed as:
Substituting d into the first equation and making the small angle approximation, one can solve for 
Note that the angle had to be converted from degrees to radians. Finally, the question asks for lines per centimeter, not meter, so the answer becomes 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources