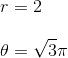All GRE Subject Test: Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #47 : Imaginary Numbers & Complex Functions
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and then combine like terms
Since each term divides by a greatest common factor of -6 reduce all of the coefficients. It would also be equivalent to divide by 6 to reduce all of the terms.
Example Question #41 : Imaginary Numbers & Complex Functions
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and then combine like terms
Example Question #291 : Gre Subject Test: Math
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and combine like terms
Example Question #12 : Complex Conjugates
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and combine like terms
Example Question #13 : Complex Conjugates
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and combine like terms
Each term divides by 2 so make sure to reduce all of the terms
Example Question #291 : Gre Subject Test: Math
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and combine like terms
Example Question #15 : Complex Conjugates
Simplify
Undefined
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and combine like terms
Since every term divides by 8 make sure to reduce all the terms by that greatest common factor
Example Question #16 : Complex Conjugates
Simplify
In problems like this, you are expected to simplify by removing i from the denominator. To do this, multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (switch the sign between the two terms from either a plus to a minus or vice versa) over itself. The conjugate over itself equals 1 and does not change the value of the expression (any number multiplied by 1 is still that number). Multiplying by the conjugate is the only way to eliminate i since there will be no middle term when we foil.
Simplify i squared to be -1 and then combine like terms
Example Question #111 : Algebra
Write the complex number 


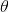
To see what the polar form of the number is, it helps to draw it on a graph, where the horizontal axis is the imaginary part and the vertical axis the real part. This is called the complex plane.

To find the angle 



Using trigonometric ratios, 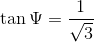

Then 
To find the distance 




Example Question #112 : Algebra
Solve:
Step 1: Re-write the log equation as an exponential equation. To do this, take the base of the log function and raise it to the number on the right side of the equal sign. This new exponent is equal to the number to the right of the log base.
Step 2: Re-write the right hand side as a power of 4..
Step 3: Re-write the equation
Step 4: We have the same base, so we can equal the exponents..
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Math Resources