All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #111 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry

Based on the pH titration curve provided, how many acidic protons are in this acid?
Four
It cannot be determined from the graph
One
Three
Two
Two
The equivalence point is the point in a titration at which the number of moles of titrant species equals the number of moles of analyte. For a polyprotic acid there are multiple equivalence points because there are more than one acidic proton in one molecule of the acid. A titration curve has as many equivalence points as the number of protons that may be neutralized by the interaction with a base. In this titration curve there are two equivalence points. The equivalence points occur when the graph has a very steep slope, and involve very large changes in pH with additions of small amounts of base. For this graph, the equivalence points occur at about pH 3.5 and 10.
Example Question #9 : Titrations
What volume in liters of 




The equivalence point in a titration is the point in which the number of moles of titrant equals to the number of moles of analyte:
We need to determine the number of moles of acetic acid we are dealing with:
Therefore, at the equivalence point there are also 0.0075 moles of 


Example Question #112 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
A 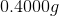



A pH indicator added to a solution causes a color change which is an indication that a reaction has reached the equivalence point. The equivalence point is when the number of moles of titrant equals the number of moles of analyte. The end point is an approximation of this in a titration.
At the equivalence point:
The number of moles of NaOH at equivalence point is calculated as follows:
Assuming we were trying to convert the number of grams of the monoprotic acid to moles, the equation would be set up as follows:
Let's plug the values we have into this equation and give the molar mass a value of 
Rearranging this equation to solve for the molar mass 
Example Question #21 : Acid Base Chemistry
What is the molarity of a 

The pH of the solution is 

![[H^{+}] = 10^{-pH}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/547894/gif.latex)
Example Question #1 : P H
What is the pH of a 

We need to calculate the pH of a 



The equation with the relationship between pH and pOH is:
We can calculate the pH by rearranging this equation:
Another way of solving this problem is shown below. The equation with the relationship between 

Rearrange this equation:
We can calculate the pH of this solution using the equation below:
Example Question #112 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
What is the pH of a 

First we need to calculate the ![[OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/595133/gif.latex)



The pOH can be calculated using the below equation:
The equation with the relationship between pH and pOH is below:
We can calculate the pH by rearranging this equation:
Another way of solving this problem is shown below. The equation with the relationship between 

Rearrange this equation:
We can calculate the pH of this solution using the equation below:
Example Question #111 : General Chemistry
Considering the 




The relationship between 


Rearranging this equation gives:
In order to calculate the 
Example Question #31 : Acid Base Chemistry
What is the pH of a 

Below is the equilibria of 



There is 100% dissociation of 


Example Question #118 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
What is the pH of a 

Below is the equilibria of 

There is 100% dissociation of 


Example Question #119 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
![]()
If 



Based on the chemical equation, 

There 


Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources






























![[OH^{-}]=2*10^{-4}\ M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/590972/gif.latex)



![K_{w}=[H_{3}O^{+}][OH^{-}]=1.0*10^{-14}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/590978/gif.latex)
![[H_{3}O^{+}]=\frac{[K_{w}]}{[OH^{-}]}=\frac{1.0*10^{-14}}{2*10^{-4}}=5*10^{-11}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/595265/gif.latex)






![[OH^{-}]=2*(5 *10^{-4} M)=0.001M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/595135/gif.latex)



![K_{w}=[H_{3}O^{+}][OH^{-}]=1.0*10^{-14}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/590961/gif.latex)
![[H_{3}O^{+}]=\frac{[K_{w}]}{[OH^{-}]}=\frac{1.0*10^{-14}}{0.001}=1*10^{-11}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/595266/gif.latex)















![[H_{3}O^{+}]=0.05M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/691497/gif.latex)
![pH=-log[H_{3}O^{+}]=-log[0.05]=1.3](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/691498/gif.latex)






![[OH^{-}]=0.10M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/691522/gif.latex)
![pOH=-log[OH^{-}]=-log[0.10]=1](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/691523/gif.latex)







![Molarity\ [H^+]=\frac{moles\ of\ solute}{Liters\ of\ solution}=\frac{2.6\ moles}{1L}=2.6M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/931418/gif.latex)
![pH=-log[H^{+}]=-log[2.59\times 10^{-4}]=3.6](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/931419/gif.latex)



