All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #23 : Reaction Chemistry
Consider the reaction reaction below.
A student allows the system to reach equilibrium and then removes two moles of hydrogen gas. Which of the following will be a result?
The amount of N2 in the reaction vessel will increase
The reaction will shift to the side with fewer total moles of gas
More NH3 will be produced
No change will occur
The reaction will first shift toward the products, then toward the reactants
The amount of N2 in the reaction vessel will increase
According to Le Chatelier's principle, when a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the system will react to restore equilibrium. In other words, it will seek to undo the stress. Here, if hydrogen gas is removed, the reaction will shift toward the reactants to re-form it. In the process, more nitrogen will be produced.
Example Question #24 : Reaction Chemistry
A saturated solution of scandium hydroxide, which also contains solid scandium hydroxide, is treated with 0.1N HCl. The addition of acid will __________ the solubility of scandium hydroxide because of __________.
decrease . . . Le Chatelier's principle
increase . . . Le Chatelier's principle
increase . . . the decreased pH
decrease . . . the common ion effect
not affect . . . the common ion effect
increase . . . Le Chatelier's principle
Scandium hydroxide dissociates according to this reaction.
As 0.1N HCl is added, it will quantitatively react with hydroxide anions to produce ScCl3 and water.
Hydroxide will be removed from the above equilibrium, and the system will compensate by shifting the equilibrium to the right, according Le Chatelier's principle. As the equilibrium shifts to the right, more solid scandium hydroxide is hydrolyzed, resulting in increased solubility.
Example Question #161 : General Chemistry
A system contains iodine atoms that are in equilibrium with respect to the reaction below:
The volume of the system is suddenly reduced, leading to an increase in pressure. What effect will this have on the reaction?
The reaction will not be affected
The reaction shifts to the left
The reaction shifts to the right
The reaction shifts to the right then to the left
The reaction shifts to the right
Since the system is originally at equilibrium and a stress is applied, Le Chatelier's principle is to be considered. By increasing the total pressure, the reaction will move in the direction toward which there are less molecules of gas.
Looking at the original reaction there are two moles of gas on the left and only one on the right, indicating that the reaction will shift to the right if the pressure is increased.
Example Question #26 : Reaction Chemistry
Consider the following saturated solution. Assume it is at equilibrium.
What is the chromate ion concentration after 0.019 moles of lead nitrate is added to 1 L of the above solution?
Us the solubility constant to calculate the answer to this question. We know that:
and
Since 


Example Question #162 : General Chemistry
Which method can be used to increase the activation energy of a reaction done in the lab?
Increasing the temperature
Increasing the pressure
Decreasing the temperature
Shaking the reaction flask
Increasing the concentration of reactants
Decreasing the temperature
The activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction. Based on the collision model, increasing the temperature, pressure, and concentration for a chemical reaction will decrease the activation energy. This is because increasing these factors increases the number of collisions of molecules, which is required for a reaction to occur. Therefore, decreasing the temperature would have the opposite effect causing the activation energy to increase, decreasing the likelihood of a reaction taking place.
Example Question #161 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
![]()
Based on the equilibrium reaction shown, how would adding 
Adding 

Adding 
Adding 

The effect of adding 
Adding 

Adding 

According to Le Chatelier's principle, if an equilibrium reaction is disturbed by addition of a reactant or product, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the disturbance. Therefore, adding 


Example Question #163 : General Chemistry
Which method can be used to decrease the activation energy of a reaction?
Increasing the concentration of reactants
Increasing the pressure
All of these
Increasing the temperature
Adding a catalyst
All of these
The activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction. Based on the collision model, increasing the temperature, pressure, and concentration for a chemical reaction will decrease the activation energy. This is because increasing these factors increases the number of collisions of molecules. Molecules must collide to react.
Example Question #163 : General Chemistry
Which of the following is true regarding the solubility product constant, 
The concentration of substance 
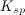
As more of substance 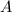


To determine the solubility product constant, we only need the concentrations and coefficients of the ions. The effective concentration of any pure substance (solid, liquid, or gas) is equal to one by definition, so does not influence the value of 
The units of the solubility product constant will depend on the coefficients of the products. 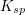
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources












![K_{sp} = [Pb^{2+}] \cdot [CrO_{4}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/348295/gif.latex)







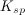
![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/73718/gif.latex)
![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100575/gif.latex)



