All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #81 : Introductory Topics
Which of the following elements has the most metallic character: 
The metallic character of elements increases as you move down a group. All of the listed elements are in Group 5. Since 
Example Question #82 : Introductory Topics
Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius: 
When looking at a periodic table, you should notice that all of these elements are in the same period. Recall that atomic radii decrease as you move right on a period. Thus, this is the order of the elements by decreasing radius:

Example Question #3 : Periodic Trends
The set of elements with the highest first ionization energies are known as which of the following?
Alkali metals
Metalloids
Noble gases
Halogens
Alkaline earth metals
Noble gases
The noble gases possess a full octet of electrons. They have the largest first ionization energies because of their tendency to keep all of their valence electrons. Halogens have the highest electron affinity; therefore, they have high—but not the highest—ionization energies. The alkali and alkaline earth metals have low electron affinities and low ionization energies. Last, the metalloids possess ionization energies that are neither high nor low.
Example Question #4 : Periodic Trends
Rank the following in order of increasing metallic character:
The correct answer is




Example Question #4 : Periodic Trends
Which of these atoms is the smallest?
Strontium
Calcium
Barium
Beryllium
Magnesium
Beryllium
The atomic radii is the size of an atom when it is not bonded to any other atoms. The periodic table can be used to estimate the size of the atomic radii of atoms. As you move down the periodic table the atomic radii increase, but as you move from left to right on the periodic table, the size of the atomic radii decrease.
Beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, and barium are all in the same group on the periodic table, so the smallest element is the element closest to the top of the periodic table since the atoms become larger as you go down the periodic table. Therefore, the smallest atom of this group is beryllium.
Example Question #2 : Periodic Trends
Which atom is the most electronegative?
Aluminium
Chlorine
Phosphorus
Silicon
Sulfur
Chlorine
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to attract and bind electrons. If the valence electrons are less then half full, then it takes less energy to lose an electron than gain electron making these atoms less electronegative. If the valence electrons are more than half full, then it takes less energy to gain electrons compared to losing an electron; therefore these electrons are more electronegative. The periodic table can be used to predict the electronegativity of the atom and how it compares to other atoms. As you move left to right of the periodic table, the electronegativity increases because the atoms on the right side of the periodic table have more valence electrons, and smaller radii. As you move down the periodic table the electronegativity decreases because the atomic number increases resulting in a greater distance between valence electrons and the nucleus causing less pull on the valence electrons.
Using the electronegativity periodic trend, we can predict which of the atom's is most electronegative. Aluminium, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, and chlorine are all in the same row in the periodic table. Therefore, chlorine is the most electronegative because it is the farthest right on the periodic table so it has the most valence electrons and it will cost less energy to gain an electron than lose an electron.
Example Question #5 : Periodic Trends
Which of the following atoms in the largest?
Sodium
Aluminium
Chlorine
Sulfur
Phosphorous
Sodium
The atomic radii is the size of an atom when it is not bonded to any other atoms. The periodic table can be used to estimate the size of the atomic radii of atoms. As you move down the periodic table the atomic radii increase, but as you move from left to right on the periodic table, the size of the atomic radii decrease.
Sodium, aluminium, phosphorus, sulfur, and chlorine are all in the same row of the periodic table. Since the size of the atomic radii decreases as you move from left to right on the periodic table, the element furthest to the left will be the largest. Therefore, sodium is the largest atom out of the group.
Example Question #2 : Periodic Trends
Which element is the least electronegative?
Selenium
Oxygen
Tellurium
Sulfur
Polonium
Polonium
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to attract and bind electrons. If the valence electrons are less then half full, then it takes less energy to lose an electron than gain electron making these atoms less electronegative. If the valence electrons are more than half full, then it takes less energy to gain electrons compared to losing an electron; therefore these electrons are more electronegative. The periodic table can be used to predict the electronegativity of the atom and how it compares to other atoms. As you move left to right of the periodic table, the electronegativity increases because the atoms on the right side of the periodic table have more valence electrons. As you move down the periodic table the electronegativity decreases because the atomic number increases resulting in a greater distance between valence electrons and the nucleus causing less pull on the valence electrons.
Using the electronegativity periodic trend, we can predict which of the atom's is least electronegative. Oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium are all in the same group of the periodic table. Therefore, polonium is the least electronegative because it is closest to the bottom of the periodic table and has the largest atomic numbers. Since polonium has the largest atomic number, there is a greater distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus resulting in a decreased pull on the valence electrons. Therefore, it is easier to lose a valence electron compared to atom's with a smaller atomic number.
Example Question #1 : Electron Configurations
What is the electron configuration for 
Cadmium normally has 


The normal electron configuration for 
Since the cadmium is losing 

Thus, the electron configuration for 
![[Kr]4d^{10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670885/gif.latex)
Example Question #2 : Electron Configurations
What is the electron configuration for 
There is no valid electron configuration for 
The normal electron configuration for 
Since it is losing 




The electron configuration for 
All College Chemistry Resources

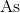
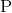














![[Kr]5s^24d^8](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670748/gif.latex)
![[Kr]5s^14d^9](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670749/gif.latex)
![[Kr]4d^{10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670747/gif.latex)
![[Kr]5s^14d^{10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670750/gif.latex)
![[Kr]4d^{10}5s^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670881/gif.latex)
![[Ar]4s^23d^4](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670788/gif.latex)
![[Ar]4s^13d^5](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670789/gif.latex)
![[Ar]3d^6](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670787/gif.latex)
![[Ar]3d^74s^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670901/gif.latex)
![[Ar]3d^6](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/670908/gif.latex)



