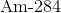All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #61 : Introductory Topics
Which of the following is not true about water?
It's molecular geometry is bent
It has a high heat capacity relative to other solvents
Its solid form is more dense than its liquid form
Its ability to make hydrogen bonds with other water molecules allows for great cohesion
It participates in many biochemical reactions
Its solid form is more dense than its liquid form
Unlike most other solvents, water is unique in that its solid form is actually less dense than its liquid form. This is precisely the reason why ice floats in water. Water does indeed participate in many biochemical reactions and can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules to allow for great cohesion. Also, the specific heat capacity of water is 

Example Question #62 : Introductory Topics
The unique properties of water, namely its incredibly high heat capacity and surface tension, can be attributed to which of the following kinds of intermolecular/intramolecular forces?
London dispersion forces
All of these
Ionic bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Van der Waals forces
Hydrogen bonding
The partial negative and positive charges on a water molecule allow it to be attracted to other polar water molecules, which creates the cohesive nature of water and contributes to its high surface tension and heat capacity. London dispersion and Van der Waals forces are significantly weaker than hydrogen bonding. Additionally, ionic bonding only occurs intramolecularly, so it has little effect on the intermolecular properties of water.
Example Question #1 : Properties Of Water
Is water an acid or a base?
Both
Acid
Base
Neither
Both
Water is an amphipathic molecule, meaning that it can act as both an acid and a base. In some situations, water can act as a Bronsted-Lowry base (defined as a species which accepts a proton). Here is an example of water acting as a base:
As you can see, 

In other situations, water can act as a Bronsted-Lowry base (defined as a species which donates a proton). Here is an example of water acting as an acid:
As you can see, 

Thus, water can act as both an acid and a base.
Example Question #2 : Properties Of Water
Which of the following substances is the least soluble in water?




Example Question #3 : Properties Of Water
Water is said to be the solvent of life due to its very unique properties. Which of the following does not represent one of the features of water that gives it uniqueness?
Liquid phase that is more dense that the solid phase
All of these represent unique characteristics of water
High heat capacity
Low surface tension
Formation of hydrogen bonds
Low surface tension
In this question, we're asked to identify an answer choice that describes something that is not a characteristic of water.
Remember that water molecules consist of a single oxygen atom with single bonds to two hydrogen atoms. There are also two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom, giving the overall molecular structure of water a bent shape. This bent shape is important, because it results in an overall net dipole moment of the water molecule, where the two hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge and the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge.
The significance of this partial charge separation is that it allows water to be excellent at forming hydrogen bonds. Recall that hydrogen bonds occur when a partially positive hydrogen atom participates in a non-covalent bond to another electronegative atom on some other molecule (though can also be intramolecular in bigger compounds, like enzymes). These intermolecular interactions between individual water molecules results in an overall strong force of attraction between them.
As a consequence of these strong hydrogen bonds between the water molecules, many unique properties of water result. For instance, liquid water has an unusually high heat capacity. Due to the strong intermolecular forces of attraction, it takes a relatively large amount of energy in order overcome the attractive forces that hold water molecules together. Another very unique property of water is that its solid phase is actually less dense than its liquid phase. Thus, when water freezes into ice, it will float to the top surface in a body of water, which is important for sustaining life in certain environments.
Finally, these strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds give water a high surface tension. Once again, the reason for this is due to the fact that it takes a relatively greater amount of energy in order to break these bonds apart. Thus, water does not have low surface tension, making this the correct choice.
Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
Isotopes differ in the number of __________.
covalent bonds
electrons
protons
lone pairs
neutrons
neutrons
By definition, isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons and electrons, but differ in the number of neutrons. This causes a difference in the mass number (protons + neutrons) as well. Neither the number of protons nor the number of electrons changes with different isotopes of the same element.
Example Question #1 : Isotopes
Which of the following is not an isotope of hydrogen?
Deuterium
Tritium
Protium
Quatrium
Quatrium
Isotopes are versions of an element with different numbers of neutrons. Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes. 


Example Question #3 : Atoms And Elements
Chromium has four naturally occurring isotopes. 











Using this information, estimate the atomic mass of chromium, in atomic mass units.
In order to find the molar mass of an atom from its isotopes and their natural abundances, use the following equation:

Since chromium has four isotopes, we will write the following equation to find its atomic mass:
Example Question #1 : Isotopes
Isotopes of a given element differ in the number of __________.
Electrons
Protons
Photons
Neutrons
Neutrons
Each element is defined by the number of protons its atoms contain. For example, hydrogen has one proton, helium has two protons, and lithium has three protons. Each element also has a characteristic number of neutrons. For example, hydrogen has zero neutrons, helium has two neutrons, and lithium has four neutrons.
Some elements, however, also have different "versions" of themselves: atoms which have a different number of neutrons, called isotopes. For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen. 


Example Question #2 : Atoms And Elements
What is the daughter nuclide when 
Recall that when a particle undergoes alpha decay, the particle is emitting an alpha particle, which is the same as 
Now, write the following equation of the alpha decay:
Thus, 
All College Chemistry Resources