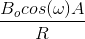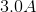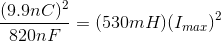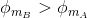All AP Physics C Electricity Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Magnetism
Two parallel wires a distance 




Relevant equations:
Step 1: Find the original and new magnetic fields created by wire 1 at wire 2, using Ampere's law with an Amperian loop of radius 

Original
New
Since the wires are parallel to each other and wire 1's field is directed circularly around it, in each case wire 1's field is perpendicular to wire 2.
Step 2: Find the original and new magnetic forces per unit length on wire 2, due to the field created by wire 1.
Original
New
So, the new force per unit length is 8 times greater than the original.
Example Question #41 : Electricity And Magnetism Exam
A region of uniform magnetic field, 

A stream of protons moving at velocity 
A semi-circular path oriented horizontally out of the page
A semi-circular path oriented horizontally into the page
A semi-circular path oriented vertically upward
A semi-circular path oriented vertically downward
A semi-circular path oriented vertically upward
The magnetic force on a moving charged particle is given by the equation:
Isolating the directional component of this equation yields the understanding that the resulting force on a moving charged particle is perpendicular to the plane of the velocity vector and magnetic field vector. Using the right-hand-rule on this cross-product shows that the velocity vector right-crossed into the magnetic field vector into the page yields a magnetic force vector upward on a positive charge. This will result in a semi-circular path oriented vertically upward.
Example Question #1 : Electromagnetism
A metal ring is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the ring. An emf of magnitude 15V is induced around the ring by increasing the field through it from zero to 5mT at a constant rate. If the area enclosed by the ring is 
Relevant equations:
Given:
Plug in (disregarding direction of emf):
Example Question #1 : Using Faraday's Law
A wire loop of area 


Relevant equations:
Write the expression for the flux using the given expression for the magnetic field strength:
Take the derivative of this flux to find the induced emf:
Determine the maximum value of 
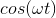
Plug this maximum induced emf into 
Example Question #2 : Electromagnetism
A wire loop carrying no current is placed near another very long straight wire carrying current 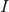

In which direction will the current induced in the small wire loop flow?
Not enough information is given to solve
No current will be induced in the wire loop
Counterclockwise
Clockwise
Clockwise
The magnetic field due to the long straight wire points into the page (right-hand rule) in the region below it in the picture. The magnitude of this magnetic field is given by:
The magnetic field thus decreases in value with increasing distance, 
According to Lenz's Law, an induced current within the wire loop will counteract this loss of magnetic flux from the straight wire. The magnetic field from the induced current in the wire loop will consequently point in the same direction as that from the current in the straight wire. The right-hand rule for a magnetic field into the page yields an induced current direction in the clockwise direction.
Example Question #51 : Electricity And Magnetism Exam
A capacitor and an inductor mH are connected in series to complete a simple circuit. The capacitor is initially charged to 9.9 nC.

What is the value of the maximum current that passes through the circuit?
Since there are no dissipative circuit elements (such as a resistor) present in the circuit, the energy originally held by the electric field of the capacitor oscillates between electric energy and magnetic energy over time. As such, the maximum electric energy of the capacitor is equal in value to the maximum magnetic energy of the inductor.
Example Question #3 : Electromagnetism
A uniform magnetic field 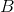

Loops A and C are the same size, with radius 


Which of the statements below is true about the values of magnetic flux through the loops due to the magnetic field?
Magnetic flux is a measure of the amount of magnetic field passing through a given area and is given by the equation:
The magnetic field is constant for this problem, and the areas are all circular loops. As such, the vector product integral simplifies to:
The angle theta is the angle between a vector normal to the surface of the area 
For loops C and D, theta is 90 degrees, so the magnetic flux for both of these loops is equal to zero.
For loops A and B, the angle theta is 0 degrees, so the magnetic flux for both of these loops is nonzero and proportional to the area of each loop. Therefore, the flux for loop B is larger than that for loop A because loop B has the larger radius.
Example Question #1 : Electric Circuits
A parallel plate capacitor has a capacitance of 

The relationship between capacitance, distance, and area is 
Now, we can use the values given in teh question to solve.
Example Question #2 : Capacitors
Charge is distributed uniformly over the area of the two plates of a parallel plate capacitor, resulting in a surface area charge density of 




Which of the following would not result in an increase in the measure of electric potential difference between the two plates?
Increase the value of the surface charge density, 
Increase the distance, 
Increase the area, 
Replace the material between the two plates with one of a lower dielectric constant,
Increase the area, 
The electric potential difference created between the plates of a parallel plate capactor is given by the equation:

The charge can be calculated by using the equation:
The value of the capacitance is related to the dimensions of the capacitor with the equation:
Combining these equations yields:
The area becomes inconsequential, while the potential is directly proportional to the surface charge density and the distance between the plates, and inversely proportional to the dielectric of the material between the plates. Changing the area does not cause any change in the potential difference measured between the plates, and changing any of the other variables would cause a resultant change in the potential difference.
Example Question #51 : Electricity And Magnetism Exam
You are hired to make a capacitor out of two parallel metal sheets. If someone wanted you to make a thin capacitor of 

For parallel plate capacitors, the equation is 
Solve for 
Now we can plug in our given values.
All AP Physics C Electricity Resources