All AP Environmental Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Global Warming
Which of the following greenhouse gases is exclusively anthropogenic?
All of these greenhouses gasses, except 

Example Question #1 : Greenhouse Gases
Which of the following are greenhouse gases?
Carbon dioxide, helium, nitrogen
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
Carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen
Helium, carbon dioxide, water vapor
All of these
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
The greenhouse effect occurs as the temperature within the Earth's atmosphere rises. Greenhouse gases trap the heat within the Earth's atmosphere. As sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it passes through the gaseous layer and the Earth's surface absorbs part of the energy and reflects some energy. These reflected rays of energy get trapped between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere. Some common greenhouse gasses include: carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and tropospheric ozone. Helium and nitrogen are two gases in the atmosphere, but they do not contribute to the greenhouse effect.
Example Question #13 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Methane produced by cattle and other livestock has potential as a renewable, alternative fuel. As commercial farmers worldwide adopt this trend, which of the following would seem a likely effect on global warming?
Since both carbon dioxide and water vapor are emitted when methane is burned, the result will be increased precipitation and increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas and even when it is burned for fuel, the emissions into the atmosphere are equally potent. Whether the methane comes out of the livestock or it is burned, it will contribute equally to global warming.
Burning the methane byproduct for fuel will utilize a potent greenhouse gas, reduce greenhouse gas input into the atmosphere and reduce dependency on energy derived from fossil fuels.
Burning the methane gas will release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing further to the greenhouse effect and warming of the planet.
When methane is burned, carbon dioxide, which is far more potent a greenhouse gas, is released into the atmosphere. Utilizing methane as fuel will exacerbate the issue of global warming.
Burning the methane byproduct for fuel will utilize a potent greenhouse gas, reduce greenhouse gas input into the atmosphere and reduce dependency on energy derived from fossil fuels.
Methane gas produced by livestock is a very potent greenhouse gas, with molecules that trap far more heat in our atmosphere than carbon dioxide. When methane is burned, carbon dioxide and water vapor are released into the atmosphere, but these vapors have a relatively benign impact on global warming when compared to the release of methane, had it not been used as fuel. Therefore, harvesting methane gas from agricultural waste and livestock prevents potent greenhouse gases from escaping into the atmosphere and also reduces dependence on energy derived from fossil fuels.
Example Question #14 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Though their atmospheric levels are much lower than those of 
CFCs are more efficient at absorbing thermal radiation.
CFCs circulate through the troposphere more quickly than 
CFCs are more difficult to remove from chimneys and tailpipes.
CFCs remain in the atmosphere for only a brief time.
CFCs do not emit from natural sources.
CFCs are more efficient at absorbing thermal radiation.
Chlorofluorocarbons, aka CFCs, are nontoxic, nonflammable chemicals containing atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine. They are used in the production of aerosol sprays, foams and packing materials, as solvents, and as refrigerants. Though mostly inert in the lower atmosphere, that low reactivity affords CFCs a lifespan that can exceed 100 years, giving them time to diffuse into the upper atmosphere and stratosphere. Once in the stratosphere, the sun's ultraviolet (or thermal) radiation is strong enough to cause the cleavage of the 
Example Question #2 : Global Warming
The greenhouse effect is responsible for many beneficial aspects of the earth's atmosphere. Which of these is NOT provided directly by the greenhouse effect?
Blocking some harmful radiation from penetrating through the atmosphere
Keeping the surface of the earth at a homogeneous temperature
All of the choices are created by the greenhouse effect
Trapping some infrared radiation from the earth within the atmosphere
All of the choices are created by the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect plays a role in all of the options because of the interaction between the layer of gasses surrounding the earth and the solar radiation that approaches the earth. An easy way to remember this is to follow the path of solar radiation traveling from the sun to the earth and think of all the possible ways in which this radiation can travel. The radiation can bounce off and not enter, it can enter and be absorbed in the surface, or it can enter and both bounce off the earth's surface and then be absorbed.
Example Question #11 : Global Warming
Choose the scientist that was not involved in studying the early existence of the greenhouse effect.
John Tyndall
Claude Pouillet
Norman Borlaug
Joseph Fourier
Norman Borlaug
Every scientist listed but Norman Burlaug are responsible for the early studies of the greenhouse effect. Joseph Fourier spoke about the effect in 1824. Claude Pouillet studied its existence further in 1827 and 1838. John Tyndall conducted experimental observations in 1859.
Example Question #17 : Global Effects And Dynamics
The term "greenhouse effect" was first coined by whom?
Svante Arrhenius
Nils Gustaf Ekholm
John Tyndall
Alexander Graham Bell
Nils Gustaf Ekholm
This term was first used by Nils Gustaf Ekholm in 1901. Ekholm was an early adopter of climate control. His early studies included how the burning of coal could add unnecessary levels of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Example Question #18 : Global Effects And Dynamics
__________ the largest contributor to greenhouse effect.
Methane
Carbon dioxide
Water vapor
Ozone
Water vapor
Water vapor is the largest contributor to greenhouse gases at 36-70%. Carbon dioxide is second with 9-26%, then methane with 4-9%, and finally ozone with 3-7%.
Example Question #12 : Global Warming
Which of the following statements regarding the greenhouse effect is true?
None of these
The greenhouse effect is only observed on Earth.
The greenhouse effect is also observed on other planets such as Mars and Venus.
The average temperature of the Earth has declined due to the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is also observed on other planets such as Mars and Venus.
The greenhouse effect can also be found on Mars, Venus, and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The effect on Venus is large because of its dense atmosphere of made of carbon dioxide.
Example Question #13 : Global Warming
Global warming can be directly and indirectly linked to many of the environmental problems we face today. Which of the answer choices would be most indirectly linked to global warming?
Habitat loss
All of the other answer choices are caused directly by global warming
Acidification of the oceans
Invasive species
Invasive species
The problems of invasive species occurs most often due to human activity, not due to a shifting global temperature average. Acidification of oceans are directly related to 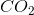
Certified Tutor
All AP Environmental Science Resources








