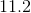All AP Environmental Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #41 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Beta diversity refers to the difference in species across habitats. If an area of particular interest has 8 different habitats and an average of 3.2 species occupying each habitat, then what would the beta diversity be?
Beta diversity is calculated by taking the total number of habitats divided by the number of species in each habitat of a given environment.
Total number of habitats:
Number of species in each habitat:
Solve:
Example Question #5 : Biodiversity
Diversity can be calculated at various scales. Which type of diversity refers to the total number of species in a geographic region that spans multiple habitats?
Alpha diversity
Delta diversity
Beta diversity
Gamma diversity
Gamma diversity
Gamma diversity refers to the total number of species within a region. This can also be referred to as regional diversity. Gamma diversity is useful in order to investigate biodiversity from a broad scale or at the landscape level.
Example Question #41 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Biological diversity is the variation between organisms in a ecosystem; both plant and animal.
What three aspects are taken into account when measuring biological diversity?
Number, variety, and variability of organisms
Number and variety of species
Number and variety of ecosystems
Location and genetics of organisms
Location and number of organisms
Number, variety, and variability of organisms
Biological diversity is concerned with not only the number, variety and variability of species within ecosystems but the number of ecosystems on the Earth and genetic diversity within species.
Example Question #7 : Biodiversity
Imagine that there is a museum that contains every species that has ever lived on planet Earth. Of all the species that have ever existed on Earth, what percentage of those are still alive today?
25%
1%
50%
10%
1%
The correct response is 1%. The majority of species that have ever lived on Earth are extinct. Mass extinctions have occurred throughout geological history due to large disturbances such as meteor crashes and ice ages. Life is fragile and disturbances can cause millions of species to go extinct rather quickly - such as most recent mass extinction when the dinosaurs disappeared. Thus, the species still alive today represent a tiny portion of the variety of life that has existed throughout the geological history of Earth.
Example Question #8 : Biodiversity
Riparian zones are important because __________.
they are centers of biodiversity, especially in arid ecosystems
they are very quickly eroded
they are one of the easiest ecosystems to manage
they cover vast areas of terrain
they are centers of biodiversity, especially in arid ecosystems
Riparian zones prevent erosion and are incredibly high in biodiversity. Riparian areas are thin and ribbon-like, accompanying streams and rivers, but often long and dense.
Example Question #46 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Which is not a value of every species on Earth?
Scientific
Comedic
Economic
Ecological
Comedic
Every species is important because of its niche in its ecosystem. Additionally, all species are potentially of scientific and medical/economic value.
Example Question #42 : Global Effects And Dynamics
Which explanation is most accurate in describing the chemical and atmospheric processes involved in ocean acidification?
Carbon dioxide is released in the atmosphere from the burning of fossil fuels, where it interacts with water vapor in the atmosphere to form carbonic acid, which enters the ocean by precipitation, lowering the pH.
Carbon dioxide is emitted by burning fossil fuels and is released into the atmosphere, increasing the atmospheric concentration of carbon. Being soluble in water, 

Sulfur produced from industrial manufacturing increases the sulfur concentration in the atmosphere, which results in sulfuric acid (
Carbon dioxide is emitted by burning fossil fuels and is released into the atmosphere, increasing the atmospheric concentration of carbon. Being soluble in water, 

Ocean acidification is most accurately described by the answer choice that talks about carbon dioxide being emitted into the atmosphere before being absorbed by ocean water to react with carbonate ions and form carbonic acid.

Image: "Ocean Acidification." NOAA PMEL Carbon Program. NOAA. Web. 6 Apr. 2015. <http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/Ocean Acidification>.
Example Question #1 : Other Ecological Consequences
Red tides are caused by a population boom of __________.
plankton
algae
bioluminescent microorganisms
cod
algae
Red tide is caused by algal blooms, which occur due to eutrophication of waterways. Red tides set off harmful chain reactions in ecosystems, because of the toxins the algae produce. The toxins get concentrated in higher trophic levels (biomagnification).
Example Question #1 : Other Ecological Consequences
Researchers have been recording the population of a species of tree frog in the Southern U.S. and have found the population to have been in steady but significant decline for the past decade. The population size is still substantial and their range in habitat extends from the East Coast to Texas. Under what category of endangerment does this species best correspond with?
Least concern
Threatened
Endangered
Near threatened
Critically endangered
Threatened
Since there has been a significant population decline over a substantial time period, but there is still an extensive range and population, this species would best be categorized as "threatened." A species classified as threatened is vulnerable to becoming endangered in the future and is still being impacted significantly by habitat loss and human activities. This frog species would be categorized as endangered if they were at immediate threat of becoming extinct.
Example Question #50 : Global Effects And Dynamics
What is the difference between "conserving" and "preserving" the environment?
Human usage
Classification of animals on the endangered species list
National park size
Animal testing of human products
Human usage
Conservationists advocate to manage resources for sustainable continued use by humans. Preservationists are in favor of prohibiting human usage rather than actively managing.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Environmental Science Resources