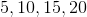All Algebra II Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #59 : Summations And Sequences
Simplify:
The iteration starts at zero and ends at three.
Substitute the terms and increase the value of 
Simplify the terms.
The answer is:
Example Question #51 : Summations And Sequences
Evaluate



The finite sequence can be restated, and evaluated, as

Example Question #61 : Summations And Sequences
Evaluate:
None of these




The finite series can be restated, and evaluated, as

Example Question #31 : Sigma Notation
Evaluate:
Substitute the value of 
Simplify each term by order of operations.
Convert all with a common denominator.
The answer is:
Example Question #2721 : Algebra Ii
List the first 4 terms of an arithmetic sequence with a first term of 3, and a common difference of 5.
An arithmetic sequence is one in which the common difference is added to one term to get the next term. Thus, if the first term is 3, we add 5 to get the second term, and continue in this manner.
Thus, the first four terms are:
Example Question #1 : Arithmetic Series
Consider the following sequence:
Find the 
This is an arithmetic sequence since the difference between consecutive terms is the same (


where 








Example Question #1 : Sequences
In the following arithmetic sequence, what is 
7
2
5
None of the other answers
6
6
The question states that the sequence is arithmetic, which means we find the next number in the sequence by adding (or subtracting) a constant term. We know two of the values, separated by one unknown value.
We know that 

The constant in the sequence is 7. From there we can go forward or backward to find out that 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Next Term In An Arithmetic Sequence
Given the sequence below, what is the sum of the next three numbers in the sequence?
By taking the difference between two adjacent numbers in the sequence, we can see that the common difference increases by one each time.
Our next term will fit the equation 

After 


Finally, after 

The question asks for the sum of the next three terms, so now we need to add them together.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Common Difference In Sequences
Which of the following cannot be three consecutive terms of an arithmetic sequence?
In each group of numbers, compare the difference of the second and first terms to that of the third and second terms. The group in which they are unequal is the correct choice.

The last group of numbers is the correct choice.
Example Question #2722 : Algebra Ii
Consider the arithmetic sequence

If 
In arithmetic sequences, the common difference is simply the value that is added to each term to produce the next term of the sequence. When solving this equation, one approach involves substituting 5 for 
so 14 is the first term of the sequence. However, a much easier approach involves only the last two terms, 

The difference between these expressions is 8, so this must be the common difference between consecutive terms in the sequence.
Certified Tutor
All Algebra II Resources







![2\sum_{n=0}^{3}-3-n = 2[(-3-0)+(-3-1)+(-3-2)+(-3-3)]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/862560/gif.latex)
![2[-3+(-4)+(-5)+-6] = 2[-18] = -36](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/862562/gif.latex)