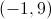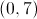All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #101 : Graphing
Give the slope of the line that passes through the 


The line cannot exist as described.
The line cannot exist as described.
The graph of 


and
This is identically false, so the graph has no 
Example Question #4 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
Give the 



The graphs of the equations do not intersect.
The graphs of the equations do not intersect.
Substitute 

The discriminant of this quadratic expression is 


The discriminant being negative, there are no real solutions to this quadratic equation. Consequently, there are no points of intersection of the graphs of the two equations on the coordinate plane.
Example Question #6 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
The graphs of the equations 





Substitute 

This quadratic equation can be solved using the 


Either 


The desired 


Example Question #102 : Graphing
Give the 


The graphs of the equations do not intersect.
Using the substitution method, set the values of 
Multiply both sides by 
Substitute in either equation:
Example Question #5 : How To Graph Inverse Variation
A line with slope 4 shares its 

This line does not exist, since the graph of 

The 




The 

To put it in standard form:
Example Question #421 : Geometry






All of the statements given in the other choices are true.




making 


and the length of long leg 


Corresponding sides of congruent triangles are congruent, so 


Also, 




Corresponding angles are congruent, so 



The false statement among the choices is that 
Example Question #894 : Act Math
What is the vertex of the function 
The 


To get the 

The vertex is 
Certified Tutor
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources