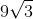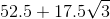All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #32 : Plane Geometry
The ratio for the side lengths of a right triangle is 3:4:5. If the perimeter is 48, what is the area of the triangle?
96
108
50
48
240
96
We can model the side lengths of the triangle as 3x, 4x, and 5x. We know that perimeter is 3x+4x+5x=48, which implies that x=4. This tells us that the legs of the right triangle are 3x=12 and 4x=16, therefore the area is A=1/2 bh=(1/2)(12)(16)=96.
Example Question #1021 : High School Math
The length of one leg of an equilateral triangle is 6. What is the area of the triangle?
The base is equal to 6.
The height of an quilateral triangle is equal to 

Example Question #32 : Plane Geometry

Figure NOT drawn to scale.



Choose the closest answer.
The altitude of a right triangle from the vertex of its right angle - which, here, is 


The similarity ratio of 

The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is the square of their similarity ratio, which here is
Therefore, the area of 
the overall area of 

Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Right Triangle
The perimeter of a right triangle is 40 units. If the lengths of the sides are 


Because the perimeter is equal to the sum of the lengths of the three sides of a triangle, we can add the three expressions for the lengths and set them equal to 40.
Perimeter:
Simplify the x terms.
Simplify the constants.
Subtract 8 from both sides.
Divide by 4
One side is 8.
The second side is

The third side is

Thus, the sides of the triangle are 8, 15, and 17.
The question asks us for the area of the triangle, which is given by the formula (1/2)bh. We are told it is a right triangle, so we can use one of the legs as the base, and the other leg as the height, since the legs will intersect at right angles. The legs of the right triangle must be the smallest sides (the longest must be the hypotenuse), which in this case are 8 and 15. So, let's assume that 8 is the base and 15 is the height.
The area of a triangle is (1/2)bh. We can substitute 8 and 15 for b and h.

The answer is 60 units squared.
Example Question #41 : Sat Mathematics
The vertices of a right triangle on the coordinate axes are at the origin, 

The triangle in question can be drawn as the following:

The lengths of the legs of the triangle are 12, the distance from the origin to 


Example Question #1 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A Right Triangle
Three points in the xy-coordinate system form a triangle.
The points are 
What is the perimeter of the triangle?
Drawing points gives sides of a right triangle of 4, 5, and an unknown hypotenuse.
Using the pythagorean theorem we find that the hypotenuse is 
Example Question #441 : Plane Geometry

Based on the information given above, what is the perimeter of triangle ABC?
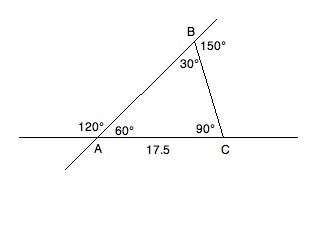
Consult the diagram above while reading the solution. Because of what we know about supplementary angles, we can fill in the inner values of the triangle. Angles A and B can be found by the following reductions:
A + 120 = 180; A = 60
B + 150 = 180; B = 30
Since we know A + B + C = 180 and have the values of A and B, we know:
60 + 30 + C = 180; C = 90
This gives us a 30:60:90 triangle. Now, since 17.5 is across from the 30° angle, we know that the other two sides will have to be √3 and 2 times 17.5; therefore, our perimeter will be as follows:
Example Question #41 : Geometry

Give the perimeter of the provided triangle.
The figure shows a right triangle. The acute angles of a right triangle have measures whose sum is 
Substituting 

This makes 
By the 45-45-90 Triangle Theorem, legs 


Also by the 45-45-90 Triangle Theorem, the length of hypotenuse



The perimeter of the triangle is
Example Question #44 : Sat Mathematics

What is the perimeter of the triangle above?
The figure shows a right triangle. The acute angles of a right triangle have measures whose sum is 
Substituting 

This makes 



Rationalize the denominator by multiplying both halves of the fraction by 
By the same reasoning, 
The perimeter of the triangle is
Example Question #43 : Geometry
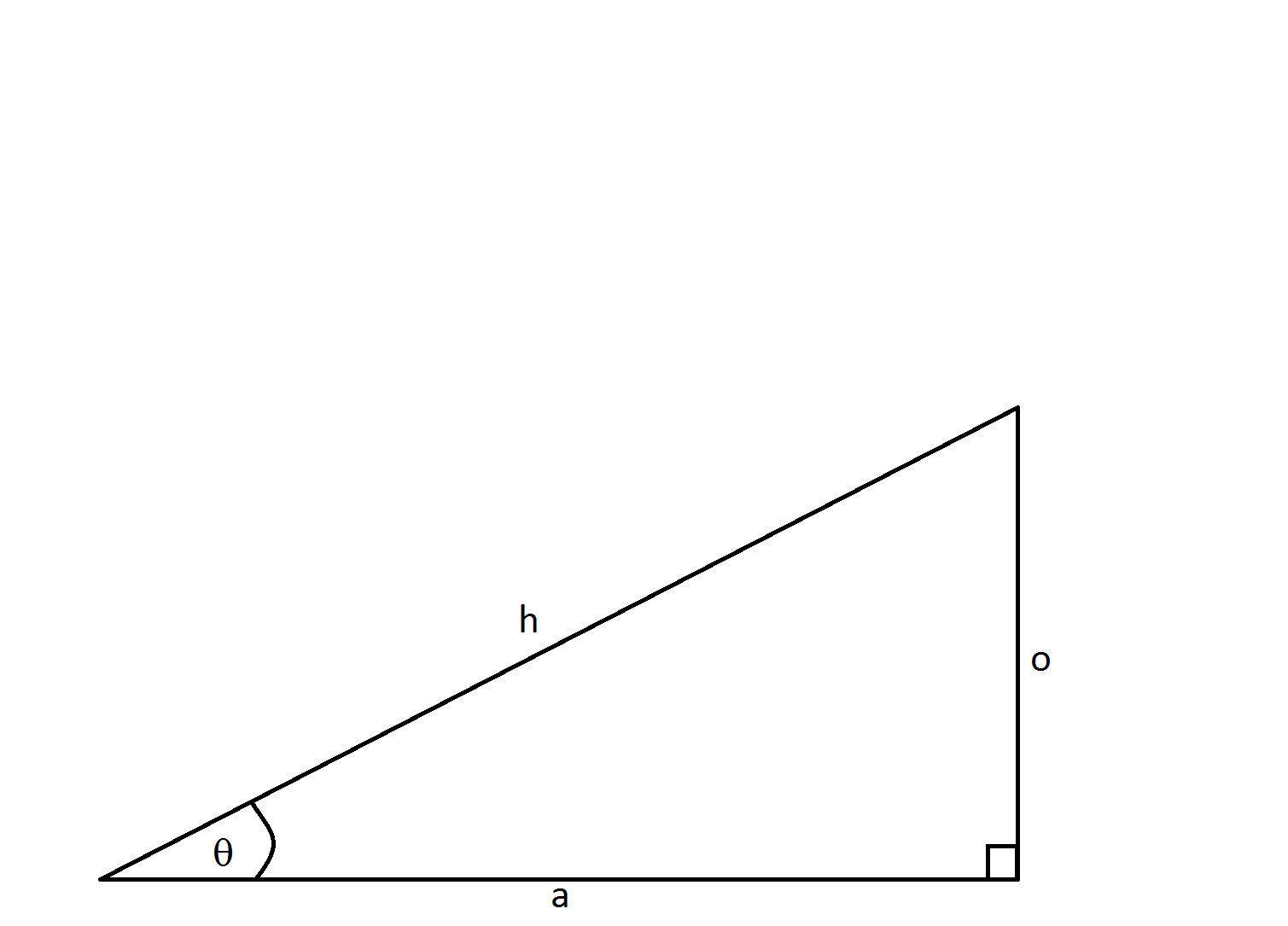
If 


Not enough information to solve
This problem is solved using the Pythagorean theorem 



Using the labels of our triangle we have:
Certified Tutor
All SAT Math Resources