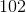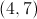All SAT II Math I Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #51 : 3 Dimensional Geometry
What is the volume of a triangular prism having a base of 2, a height of 8, and second height of 14?
To find the volume of a triangular prism we use the equation
In our case our
Therefore,
Example Question #2 : Other 3 Dimensional Geometry
If a cube has a surface area of 
The longest diagonal of a cube transverses the interior of the figure:

This distance is defined by the super pythagorean theorem :
where 


We can use the given surface area to find the length of the side:

We can use this value for the side to plug into the super pythagorean theorem
Which can be simplified to
Example Question #6 : How To Graph An Ordered Pair
Which of the following points is in Quadrant IV on the coordinate plane?
Two of these points are in Quadrant IV.
Quadrant IV consists of the points with positive 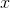


Example Question #132 : Geometry
Give the axis of symmetry of the parabola of the equation
The line of symmetry of the parabola of the equation
is the vertical line
Substitute 
The line of symmetry is
That is, the line of the equation 
Example Question #571 : Sat Subject Test In Math I
What is the center of the circle with the following equation?
Remember that the basic form of the equation of a circle is:
This means that the center point 
Therefore, the center is
Example Question #2 : Coordinate Geometry
What is the area of the sector of the circle formed between the 

Round your answer to the nearest hundreth.
For this question, we will need to do three things:
- Determine the point in question.
- Use trigonometry to find the area of the angle in question.
- Use the equation for finding a sector area to finalize our answer.
Let us first solve for the coordinate by substituting into our equation:
Our point is, therefore:
Now, we need to calculate the angle formed between the origin and the point that we were given. We can do this using the inverse tangent function. The ratio of 

Therefore, the angle is:
To solve for the sector area, we merely need to use our standard geometry equation. Note that the radius of the circle, based on the equation, is 
This rounds to 
Example Question #3 : Coordinate Geometry
What is the area of the sector of the circle formed between the 

Round your answer to the nearest hundreth.
For this question, we will need to do three things:
- Determine the point in question.
- Use trigonometry to find the area of the angle in question.
- Use the equation for finding a sector area to finalize our answer.
Let us first solve for the coordinate by substituting into our equation:
Our point is, therefore:
Now, we need to calculate the angle formed between the origin and the point that we were given. We can do this using the inverse tangent function. The ratio of 

Therefore, the angle is:
To solve for the sector area, we merely need to use our standard geometry equation. Note that 

This rounds to 
Example Question #1 : Parabolas And Circles
If the center of a circle is at 


Since you are looking for a point on the 

The center of the circle is at the origin and radius is the distance from the center, so that means the point you are looking for must be 

This can be two points on the 

Example Question #1 : Coordinate Geometry
Given a point 


The displacement between negative three and positive one is four.
This mean that after flipping the point, it must be symmetrical to its original location. The new point must also be 4 units to the right of the line.
The new point would be located at:
The answer is:
Example Question #4 : Coordinate Geometry
Which of the following symmetries applies to the graph of the relation

I) Symmetry with respect to the origin
II) Symmetry with respect to the 
III) Symmetry with respect to the 
None of these
II only
I only
III only
I, II and III
III only
The relation
is a circle with center 

In other words, it is a circle with center at the origin, translated right 

or
is this circle translated right zero units and up 2 units. The upshot is that the circle moves along the 


Certified Tutor
All SAT II Math I Resources