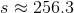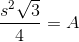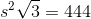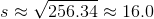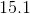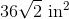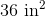All PSAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Tetrahedrons
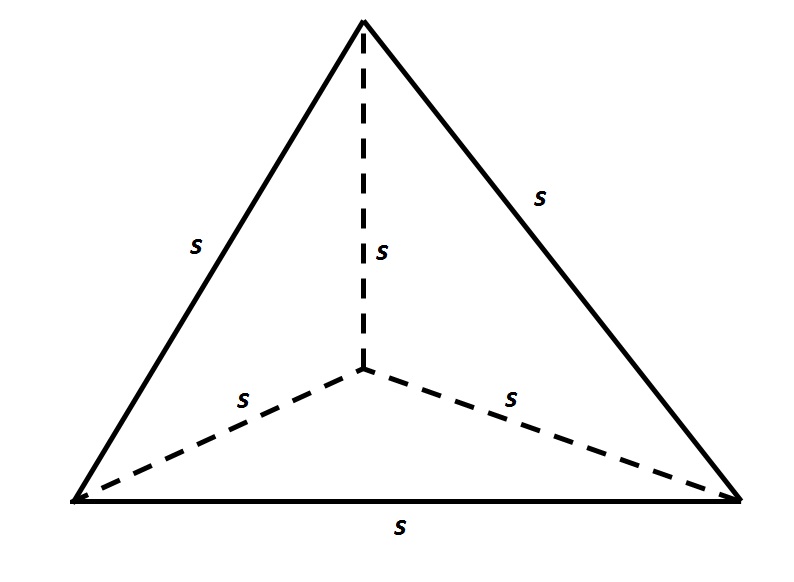
Refer to the above tetrahedron, or four-faced solid. The surface area of the tetrahedron is 444. Evaluate 
The tetrahedron has four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 

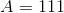
Example Question #1 : Tetrahedrons

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
The above triangular pyramid has volume 25. To the nearest tenth, evaluate 
Insufficient information is given to answer the problem.
We are looking for the height of the pyramid.
The base is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 4, so its area can be calculated as follows:
The height 
We set 


Example Question #252 : Geometry

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
Give the volume (nearest tenth) of the above triangular pyramid.
The height of the pyramid is 
The volume of a pyramid can be calculated using the fomula
Example Question #1 : Tetrahedrons
A regular tetrahedron has an edge length of 
The volume of a tetrahedron is found with the equation 

Plug in 4 for the edge length and reduce as much as possible to find the answer:
The volume of the tetrahedron is 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Tetrahedron
A regular tetrahedron has four congruent faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle.
A given tetrahedron has edges of length six inches. Give the total surface area of the tetrahedron.
The area of an equilateral triangle is given by the formula
Since there are four equilateral triangles that comprise the surface of the tetrahedron, the total surface area is
Substitute 

Example Question #2 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Tetrahedron

Give the surface area of the above tetrahedron, or four-faced solid, to the nearest tenth.
Insufficient information is given to answer the question.
The tetrahedron has four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 7. Each face has area
The total surface area is four times this, or about 
Rounded, this is 84.9.
Certified Tutor
All PSAT Math Resources