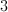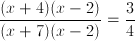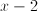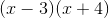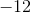All PSAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #31 : Variables
Which of these expressions can be simplified further by collecting like terms?
None of the expressions in the other choices can be simplified further
None of the expressions in the other choices can be simplified further
A binomial can be simplified further if and only if the two terms have the same combination of variables and the same exponents for each like variable. This is not the case in any of the four binomials given, so none of the expressions can be simplified further.
Example Question #1 : Binomials
Solve for .
Factor the expression
numerator: find two numbers that add to 2 and multiply to -8 [use 4,-2]
denominator: find two numbers that add to 5 and multiply to -14 [use 7,-2]
new expression:
Cancel the and cross multiply.
Example Question #22 : Polynomials
Give the coefficient of in the product
While this problem can be answered by multiplying the three binomials, it is not necessary. There are three ways to multiply one term from each binomial such that two terms and one constant are multiplied; find the three products and add them, as follows:
Add:
The correct response is .
Example Question #291 : Variables
Give the coefficient of in the binomial expansion of .
If the expression is expanded, then by the binomial theorem, the term is
or, equivalently, the coefficient of is
Therefore, the coefficient can be determined by setting
:
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Value Of The Coefficient
Give the coefficient of in the binomial expansion of .
If the expression is expanded, then by the binomial theorem, the term is
or, equivalently, the coefficient of is
Therefore, the coefficient can be determined by setting
:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Value Of The Coefficient
Give the coefficient of in the binomial expansion of .
If the expression is expanded, then by the binomial theorem, the term is
or, equivalently, the coefficient of is
Therefore, the coefficient can be determined by setting
Example Question #5 : Binomials
Give the coefficient of in the product
.
While this problem can be answered by multiplying the three binomials, it is not necessary. There are three ways to multiply one term from each binomial such that two terms and one constant are multiplied; find the three products and add them, as follows:
Add:
The correct response is -122.
Example Question #41 : Algebra
Give the coefficient of in the product
.
While this problem can be answered by multiplying the three binomials, it is not necessary. There are three ways to multiply one term from each binomial such that two terms and one constant are multiplied; find the three products and add them, as follows:
Add: .
The correct response is .
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Multiply the binomial.
By multiplying with the foil method, we multiply our first values giving , our outside values giving . our inside values which gives , and out last values giving .
Example Question #1 : How To Factor A Trinomial
Factor the following expression completely:
We must begin by factoring out from each term.
Next, we must find two numbers that sum to and multiply to .
Thus, our final answer is:
Certified Tutor
All PSAT Math Resources