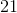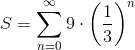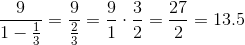All Precalculus Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #4 : Partial Sums Of Series
In case you are not familiar with summation notation, note that:
What is the value of 
Because the iterator starts at 

Now expanding the summation to show the step by step process involved in answering the question we get,

Example Question #1 : Finding Sums Of Infinite Series
Find the value for
To best understand, let's write out the series. So
We can see this is an infinite geometric series with each successive term being multiplied by 
A definition you may wish to remember is





Example Question #191 : Pre Calculus
Evaluate:
The series does not converge.
This is a geometric series whose first term is 

Example Question #2 : Finding Sums Of Infinite Series
Evaluate:
The series does not converge.
This is a geometric series whose first term is 

Example Question #191 : Pre Calculus
What is the sum of the following infinite series?
diverges
This series is not alternating - it is the mixture of two geometric series.
The first series has the positive terms.
The second series has the negative terms.
The sum of these values is 3.5.
Example Question #31 : Sequences And Series
What is the sum of the alternating series below?
The alternating series follows a geometric pattern.
We can evaluate the geometric series from the formula.
Example Question #6 : Sums Of Infinite Series
Find the sum of the following infinite series:
Notice that this is an infinite geometric series, with ratio of terms = 1/3. Hence it can be rewritten as:
Since the ratio, 1/3, has absolute value less than 1, we can find the sum using this formula:
Where 

Example Question #3 : Sums Of Infinite Series
In the infinite series 



210
128
-64
170
-256
170
Once you're identified the pattern in the series, you might see a quick way to perform the summation. Since the base of the exponent for each term is negative, the result will be positive if 
-2, 4, -8, 16, -32, 64, -128, 256
Note that each "pair" of adjacent numbers has one negative and one positive. for the first pair, -2 + 4 = 2. For the second, -8 + 16 = 8. For the third, -32 + 64 = 32. And so for the fourth, -128 + 256 = 128. You can then quickly sum the values to see that the answer is 170.
Example Question #2 : Introductory Calculus
At what value of 

There is no hole
To find discontinuity we need to look at where the denominator of the function is equal to zero. Looking at our function,

we need to set the denominator equal to zero and solve for 
When 

Therefore 
Example Question #1 : Limits
What is the

The limit does not exist
Means to find the limit of the function as 






Certified Tutor
All Precalculus Resources