All Precalculus Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Find The Amplitude Of A Sine Or Cosine Function
Find the amplitude of the following trig function:
Rewrite 
The absolute value of 
Example Question #53 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions
Find the amplitude of the function.
For the sine function

the amplitude is given as 
As such the amplitude for the given function


Example Question #1841 : High School Math
Which of the given functions has the greatest amplitude?
The amplitude of a function is the amount by which the graph of the function travels above and below its midline. When graphing a sine function, the value of the amplitude is equivalent to the value of the coefficient of the sine. Similarly, the coefficient associated with the x-value is related to the function's period. The largest coefficient associated with the sine in the provided functions is 2; therefore the correct answer is 
The amplitude is dictated by the coefficient of the trigonometric function. In this case, all of the other functions have a coefficient of one or one-half.
Example Question #1 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Given the function 

For the function 
Recall that the parent function 


Set the inner quantity of 
This indicates that there is a zero at 



Example Question #2 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Which of the choices represents asymptote(s), if any?
Factor the numerator and denominator.
Notice that the 

The denominator cannot be equal to zero. Set the denominator to find the location where the x-variable cannot exist.
The asymptote is located at 
Example Question #71 : Graphs And Inverses Of Trigonometric Functions
Find the vertical asymptote of the equation.
There are no vertical asymptotes.
To find the vertical asymptotes, we set the denominator of the function equal to zero and solve.
Example Question #1 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Given the function 

Example Question #5 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Given the function 

Example Question #6 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Which of the following represents the asymptotes for the general parent function 
If you do not have these asymptotes memorized, they can be easily derived. Write 

Now we need to solve for 





Example Question #1 : Find The Equations Of Vertical Asymptotes Of Tangent, Cosecant, Secant, And Cotangent Functions
Assume that there is a vertical asymptote for the function 



We know that the parent function 


Now we will add this to the parent function equation for vertical asymptotes
Now we will set this equation for the given vertical asymptote at
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Precalculus Resources









































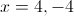









 has vertical asymptotes at
has vertical asymptotes at  where
where  is any integer. We will set the quantity inside the
is any integer. We will set the quantity inside the  function equal to zero to solve for the shift of the asymptote.
function equal to zero to solve for the shift of the asymptote.







 has asymptotes at
has asymptotes at  where
where  is any integer. We will set the quantity within the
is any integer. We will set the quantity within the  function equal to zero in order to find the shift of the asymptote.
function equal to zero in order to find the shift of the asymptote. 























