All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Enzymes And Enzyme Inhibition
In order to catalyze a reaction, an enzyme is required to __________.
increase the activation energy
increase the equilibrium constant
be saturated with substrate
decrease the activation energy
decrease the activation energy
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are responsible for the acceleration of the rate and specificity of many metabolic reactions. In order for rate acceleration to occur, an enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction. This allows for products to be formed more quickly and reactions to reach equilibrium more rapidly. Substrates bind to the active site of an enzyme and, in the presence of a large concentration of substrate, enzyme active sites become saturated and the reaction rate reaches a maximum constant. The equilibrium constant is calculated from the expression for chemical equilibrium, and is not affected by enzymes. Thus, the correct answer is to decrease the activation energy.
Example Question #221 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher binding affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
In comparison to the adult oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, the fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve will __________.
be shifted to the right and display a higher Km
be shifted to the right and display a lower Km
be shifted to the left and display a higher Km
be shifted to the left and display a lower Km
be shifted to the left and display a lower Km
Fetal hemoglobin is associated with a left-shift due to its greater binding affinity for oxygen. The Michaelis constant, Km, is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is 0.5 * Vmax. A low Km indicates high substrate affinity.
Example Question #2 : Enzymes And Enzyme Inhibition
Which of the following is NOT a class of enzyme?
Hydrolase
Isomerase
Pyrimidine complex
Ligase
Transferase
Pyrimidine complex
The correct answer is pyrimidine complex. A pyrimidine refers to a type of nucleotide base. Enzymes commonly have the suffix -ase at the end of their name.
Example Question #51 : Proteins
Functions of enzymes include all of the following except __________.
shifting the equilibrium of a reaction
shifting substrates into more favorable positions in the active site
lessening the time required for a reaction to take place
catalyzing both forward and reverse reactions
decreasing the activation energy of a reaction
shifting the equilibrium of a reaction
Enzymes are unable to shift the equilibrium of a reaction. This is a commonly confused enzyme concept, but it should be known that, chemically speaking, only adding or removing reactants and/or products can shift the equilibrium of a reaction. Although this concept is mainly seen in chemisty, known as Le Chatelier's principle, this principle is surprisingly helpful and applicable to many fields of science, including biology. All other answer choices are functions of enzymes.
Example Question #52 : Proteins
Which of the following would most greatly increase the activity of an enzyme functioning in the small intestine?
Decrease the pH
Increase the amount of enzymes
Increase the amount of substrate
Decrease the temperature
Increase the amount of substrate
The rate of enzymatic activity can be increased in a few ways. Enzymes have optimal levels of acidity and temperature at which they function best. If this optimal level is exceeded, the enzyme will denature. Enzymes of the small intestine are adjusted to a relatively alkaline environment and will denature in acidic environments. Decreasing the temperature would decrease the rate of catalyzation. By increasing the amount of substrate, the enzyme will function faster. The level at which an enzyme's rate of catalyzation can no longer be made faster by the addition of substrate is referred to as its Vmax.
Example Question #51 : Proteins
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase exhibits typical enzyme kinetics expected of similar enzymes. Which of the following is the quantity described by the value Km?
The volume of inhibitor necessary to reduce the catalyzed reaction rate by half
The enzyme concentration necessary to achieve half maximum reaction rate
The half maximum reaction rate with enzyme catalysis
The time it takes to reach half maximum reaction rate under standard conditions
The substrate concentration necessary to achieve half maximum reaction rate
The substrate concentration necessary to achieve half maximum reaction rate
Reaction rates are generally impacted by the concentration of the reactants in the reaction. The Km is the amount of substrate needed to attain a concentration resulting in half of the maximum rate achievable by an ezyme catalyzed reaction.
The maximum rate will be limited by the number of enzyme moleules available, and will be reached when the enzyme active sites are saturated.
Example Question #53 : Proteins
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
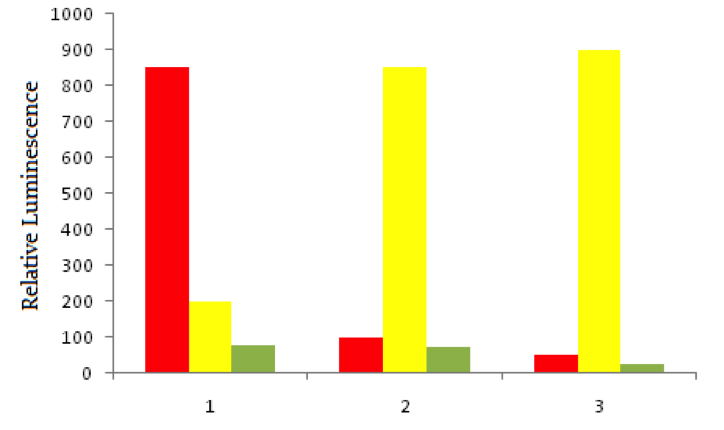
Cancer cells often invade by breaking through the collagen of a basement membrane of epithelial tissue. Considering the composition of basement membranes, which of the following compounds is most likely to be used by cancer cells for this purpose?
Synthase
Peroxidase
Lipase
Amylase
Protease
Protease
The basement membrane and sub-basement structures are predominately made of protein (connective tissue). To infiltrate this region, a protease would be most appropriate. The remaining choices are all enzymes, but would not be capable of digesting appropriate proteins.
Example Question #11 : Enzymes And Enzyme Inhibition
Which amino acid has a side chain that can form covalent bonds?
Cysteine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Glycine
Histidine
Cysteine
Cysteine has a sulfide (-SH) in its side chain, which can form covalent disulfide bonds. These bonds are often integral in creating protein tertiary structures.
Example Question #61 : Proteins
A supercoiled helix is described by which level of peptide structure?
Quartenary
Secondary
Tertiary
Primary
There is not enough information to tell
Secondary
Secondary peptide structure refers to alpha-helices and beta-sheets, which are formed by hydrogen bonding. A supercoiled helix is due to the secondary structure of a peptide. Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids, tertiary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the protein, and quatenary structure arises when more than one peptide subunit interacts.
Example Question #222 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
Disulfide linkages are connections made between polypeptide chains to increase the cohesion of a protein. These bonds fall into the category of __________.
hydrogen bonds
covalent bonds
ionic bonds
metallic bonds
covalent bonds
Disulfide bonds are covalent attachments created between two sulfur atoms. Cysteine is usually the amino acid that creates these connections.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




