All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

T-cells use receptors in their activity to defend their biological hosts. These receptors are protein molecules, heavily modified before being sent to the cell's surface. In which organelle does the majority of such modification take place?
Nucleolus
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is the organelle tasked specifically with the modification of proteins. Membrane proteins are synthesized by ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum before being sent to the Golgi apparatus for modification and packaging. This packaging allows for integration of the receptor proteins into the membrane.
Example Question #1 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
A vesicle travelling from the __________ back to the endoplasmic reticulum is most likely contains a __________ protein coat.
Golgi body . . . COPI
Golgi body . . . clathrin
plasma membrane . . . COPII
plasma membrane . . . COPI
Golgi body . . . COPI
There are three common vesicle protein coats: clathrin, COPI, and COPII. Vesicles coated in clathrin are typically being sent from the Golgi to the plasma membrane or endosomes. COPII vesicles are headed from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi body. Vesicles coated in COPI are typically involved in retrograde transport from the Golgi body to the endoplasmic reticulum (recycling proteins).
Example Question #4 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
Which of the following choices describe functions of the Golgi apparatus?
I. Post-translational modifications
II. Formation of lysosomes
III. Carbohydrate synthesis
IV. Protein trafficking
I, II, III, and IV
I and IV
II, III, and IV
I, II, and III
I, II, III, and IV
Every choice describes one of the diverse functions of the Golgi apparatus. It is a crucial organelle for protein trafficking via the secretory pathway. It also serves as one of the first steps of lysosome formation, by organizing lysosomal proteins and making vesicles that will eventually become mature lysosomes. The Golgi is also responsible for various post-translational modifications, including processing of glycosylation. Carbohydrate synthesis also occurs in the Golgi, facilitating glycosylation and other modification pathways.
Example Question #2 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
What is the difference between cytosolic ribosomes and ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
RER ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, while cytosolic ribosomes synthesize proteins that are to be localized in a membrane or to be excreted from a cell
Cytosolic ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, while RER ribosomes synthesize proteins that are to be localized in a membrane or to be excreted from a cell
There is no difference between them
RER ribosomes are located in the nucleus
Cytosolic ribosomes require a peptidyl transferase
Cytosolic ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, while RER ribosomes synthesize proteins that are to be localized in a membrane or to be excreted from a cell
While both types of ribosomes are used to make proteins, the difference between them has to do with the fate of the proteins. Cytosolic ribosomes make proteins for the cytosol, which rough endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes make them to be bound in membranes, or to be excreted from the cell in vesicles (exocytosis). Both types of ribosmes require a peptidyl transferase to elongate the peptide chain during protein synthesis.
Example Question #1 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
Scientists identify a mutation in an isolated community in central Africa that prevents individuals from detoxifying potentially harmful organic molecules, leading to a high percentage of people who become very ill after consuming alcohol. What cellular organelle does this mutation most likely affect the most?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysozome
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum functions in drug and alcohol detoxification. A common incorrect answer chosen here is the lysozome, which digests food, bacteria, viruses, and damaged organelles or cellular structures.
Example Question #5 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
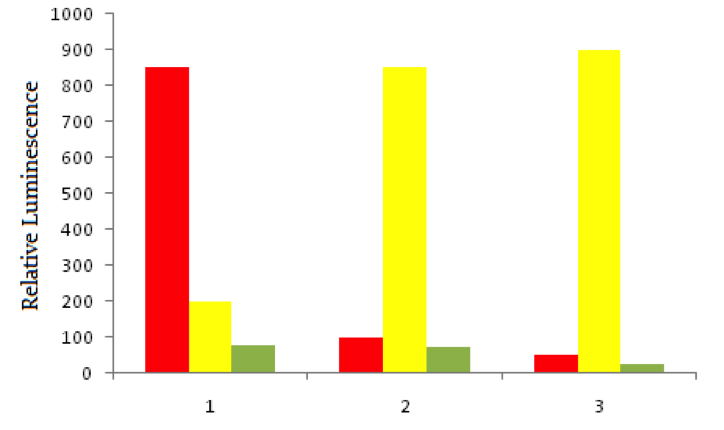
A scientist discovers that there is a class of proteins called tumor suppressors. These proteins are present in the cytosol of almost all human cells, and serve to downregulate cell division by preventing entry into key parts of the cell cycle. Where are these proteins most likely synthesized?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus
Cytosolic ribosomes
Mitochondria
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytosolic ribosomes
Tumor suppressors, as defined in the question, are proteins. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes. While the rough endoplasmic reticulum contains ribosomes, its function is related to the synthesis of transmembrane and extra-cellular proteins. Cytosolic ribosomes will be responsible for synthesis of proteins that remain in the cell.
Example Question #51 : Cellular Structures And Organelles
Which of the following cellular components synthesizes lipids of the plasma membrane?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Mitochondria
Ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lipids that are usually used for the cell membrane are created in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes are involved in protein production. The mitochondria are essential in producing ATP.
Example Question #2 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
In 2013, scientists linked a cellular response called the unfolded protein response (UPR) to a series of neurodegenerative diseases, including such major health issues as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease. According to their work, the unfolded protein response is a reduction in translation as a result of a series of enzymes that modify a translation initiation factor, eIF2, as below:
![]()
In the above sequence, the unfolded protein sensor binds to unfolded protein, such as the pathogenic amyloid-beta found in the brains of Alzheimer’s Disease patients. This sensor then phosphorylates PERK, or protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase. This leads to downstream effects on eIF2, inhibition of which represses translation. It is thought that symptoms of neurodegenerative disease may be a result of this reduced translation.
Regarding unfolded proteins discussed in the passage, which organelle is likely to be the site of initial protein folding in normal cells?
Lysosome
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus
Endoplasmic reticulum
Protein folding takes place in the endoplasmic reticulum, typically coinciding with the translation by bound ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Further modification can take place in the Golgi. Note that ribosomes in the cytosol or on the rough endoplasmic reticulum may translate a protein, but the protein folding will occur in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Example Question #1 : Endoplasmic Reticulum And Golgi Body
The liver is one of the major sites for drug metabolism and detoxification. Which organelle would you expect to play an important role in this process?
Mitochondria
Golgi body
Lysosomes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
One of the major functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is drug metabolism. In the liver, the cellular smooth endoplasmic reticulum serves as the primary site of drug and alcohol detoxifiction. This organelle is present (and active) in cells throughout the body, but plays the most impactful role in the cells of the liver. While lysosomes are responsible for clearing cellular debris, they commonly digest pathogens and microbes rather than chemical contaminants, like drugs or alcohol.
Example Question #1261 : Biology
In eukaryotic cells, what organelle is associated with translation of antibody proteins?
Endoplasmic reticulum
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic reticulum
Antibody proteins are translated by ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and subsequently secreted out of the cell in vesicles. While the Golgi apparatus is involved in the secretory pathway of these proteins, it is not specifically involved in the translation.
The nucleus and mitochondria are not associated with antibody protein translation.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




