All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #61 : Dna, Rna, And Proteins
One component of the immune system is the neutrophil, a professional phagocyte that consumes invading cells. The neutrophil is ferried to the site of infection via the blood as pre-neutrophils, or monocytes, ready to differentiate as needed to defend their host.
In order to leave the blood and migrate to the tissues, where infection is active, the monocyte undergoes a process called diapedesis. Diapedesis is a process of extravasation, where the monocyte leaves the circulation by moving in between endothelial cells, enters the tissue, and matures into a neutrophil.
Diapedesis is mediated by a class of proteins called selectins, present on the monocyte membrane and the endothelium. These selectins interact, attract the monocyte to the endothelium, and allow the monocytes to roll along the endothelium until they are able to complete diapedesis by leaving the vasculature and entering the tissues.
The image below shows monocytes moving in the blood vessel, "rolling" along the vessel wall, and eventually leaving the vessel to migrate to the site of infection.

The maturation of monocytes into neutrophils requires the expression of new segments of DNA. The expression of these genes is mediated by demethylation of the needed DNA sequences. This is an example of __________.
epigenetic modification
translational modification
DNA splicing
transcriptional modification
RNA splicing
epigenetic modification
Any change to the DNA itself that modifies expression without changing the base sequence can be thought of as an epigenetic change. Methylation and demethylation are common types of epigenetic modification.
Example Question #2 : Regulation Mechanisms And Epigenetics
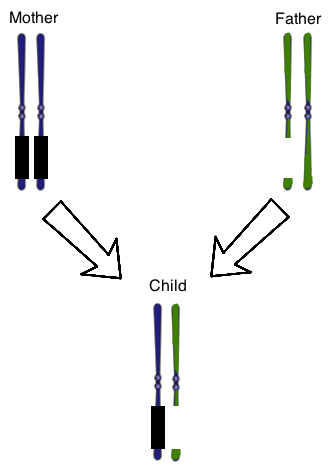
The concept of genomic imprinting is important in human genetics. In genomic imprinting, a certain region of DNA is only expressed by one of the two chromosomes that make up a typical homologous pair. In healthy individuals, genomic imprinting results in the silencing of genes in a certain section of the maternal chromosome 15. The DNA in this part of the chromosome is "turned off" by the addition of methyl groups to the DNA molecule. Healthy people will thus only have expression of this section of chromosome 15 from paternally-derived DNA.
The two classic human diseases that illustrate defects in genomic imprinting are Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes. In Prader-Willi Syndrome, the section of paternal chromosome 15 that is usually expressed is disrupted, such as by a chromosomal deletion. In Angelman Syndrome, maternal genes in this section are deleted, while paternal genes are silenced. Prader-Willi Syndrome is thus closely linked to paternal inheritance, while Angelman Syndrome is linked to maternal inheritance.
Figure 1 shows the chromosome 15 homologous pair for a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome. The parental chromosomes are also shown. The genes on the mother’s chromosomes are silenced normally, as represented by the black boxes. At once, there is also a chromosomal deletion on one of the paternal chromosomes. The result is that the child does not have any genes expressed that are normally found on that region of this chromosome.
Histones are proteins that can interact with some sequences of DNA to help it coil into a more manageable arrangement within the nucleus. If the DNA-histone interaction is mediated primarily by intermolecular bonds, which of the following is likely true of histones?
They are basic and depend on dipole interactions
They are neutral and depend on van der Waals interactions
They are basic and depend on covalent interactions
They are acidic and depend on covalent interactions
They are acidic and depend on dipole interactions
They are basic and depend on dipole interactions
DNA is acidic, and thus has a generally negative charge in aqueous conditions (consider what this means for the electrophoresis pattern of DNA in an agarose gel). Because the interaction has to be tight to coil DNA effectively, it must be a dipole interaction. Dipole interactions are relatively strong intermolecular forces. Covalent forces, however, are intramolecular and much more permanent than dipole interactions.
Acidic DNA has a negativecharge, which will be drawn to a basic histone with a positive charge.
Example Question #361 : Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, And Genetics
A competitive inhibitor for RNA polymerase III would have the most significant direct effect on which of the following?
Translation
Replication
None of these
Transcription
Replication, transcription and translation
Translation
RNA polymerase III is used to transcribe tRNA. tRNA is used to carry amino acids to ribosomes where they can be used for translation.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




