All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #17 : Analyzing Reactions
Which of the following would be considered a Lewis base?
A lewis base is an electron pair donor. 

Example Question #18 : Analyzing Reactions
Which of the following types of reactions best describes the following reaction:
Double replacement
Redox reaction
Combination
Catalytic
Combustion
Redox reaction
A redox reaction is also known as an oxidation/reduction reaction. This type of reaction involves the transfer of electrons from on reactant to another. In this reaction, an electron is transferred from 



Example Question #2 : Oxidation Reduction Analysis
What is the oxidation state of manganese in 
In this compound oxygen has an oxidation number of 







Simplifying the above equation:
Rearranging to solve for 
Example Question #19 : Analyzing Reactions
What is the oxidation state of manganese in 
In this compound oxygen has an oxidation number of 









Simplifying the above equation:
Rearranging to solve for 
Example Question #1 : Titration Procedure And Indicators
250mL of 2N 

Neutral and green
Basic and green
Acidic and yellow
Basic and yellow
Acidic and green
Acidic and green
Each of these compounds requires one equivalent of H+ is added to 100mL of 5N NH3 mol, so for HClO4, 2N = 2M, and for NH3, 5N = 5M.
Using the concentrations and volumes, we can find the moles, finding 

In this case, equivalents of acid are equal to the equivalents of base, meaning that we are at the equivalence point in a titration. HClO4 is a strong acid, and NH3 is a weak base.
Thus, the acid will fully dissociate, while the base will not, resulting in a greater concentration of H+ than OH– in the solution. This means the resulting solution will be acidic. We know that the indicator changes from yellow to green at 8.3, which is a basic pH. Our initial solution is basic, and we must pass through the pH of 8.3 to reach our final acidic solution, with pH < 8.3, meaning that the indicator must change from yellow to green during the reaction. This gives out final answer that the solution will be acidic and green.
Example Question #301 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry
Given the unbalanced equation below, how many grams of carbon dioxide will be produced from one mole of glucose and three moles of oxygen?
The first step to solve will be to balance the chemical reaction:
We see that we see that for every one mole of glucose used, six moles of carbon dioxide will be made. Similarly, for every six moles of oxygen used, six moles of carbon dioxide will be formed. For the reaction to carry out to completion, however, there must exist six moles of oxygen for every one mole of glucose. In the problem's circumstances, one of these compounds becomes the limiting reactant, in this case it is oxygen.
We only have three moles of oxygen, but we would need six to react all the given glucose, making oxygen the limiting reagent. We need to find the carbon dioxide produced from the limited amount of oxygen present. Use the molar ratio between oxygen and carbon dioxide and the molar mass of carbon dioxide to solve.
Example Question #42 : Analytical Chemistry
Household vinegar contains the organic compound acetic acid with chemical formula, 



Density of vinegar is the following:
Convert the moles of 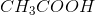
To calculate the percentage of 
Therefore,
Example Question #1 : Solubility And Precipitation
Consider the following balanced equation for the solubility of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.
What is the solubility of barium hydroxide?
In order to solve for the solubility of barium hydroxide, we need to establish an ICE table for the reaction.
I. Initially, there are no barium ions or hydroxide ions in the solution, so we can call their concentrations zero at the beginning of the reaction.
C. For every molecule of dissolved barium hydroxide, there will be one ion of barium and two ions of hydroxide. As a result, the increases in each ion can be designated 

E. Finally, we plug these values into the equilibrium expression and set it equal to the solubility product constant.
Example Question #43 : Analytical Chemistry
Write the solubility product, 

The solubility product constant (

The denominator represents solid barium sulfate which is considered a constant. When the equation is rearranged, it becomes:
The product, ![K_{eq}*[BaSO_{4}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553151/gif.latex)

Example Question #44 : Analytical Chemistry
Write the solubility product, 

The solubility product constant (

The denominator represents solid barium sulfate which is considered a constant. When the equation is rearranged, it becomes:
The product, ![K_{eq}*[AgCN]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553036/gif.latex)

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources


































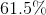
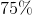












![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94058/gif.latex)
![\small 5*10^{-3} = [x][2x]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126927/gif.latex)

![K_{sp} = [Ba]^{4+}[SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553588/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba]^{2+}[SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541641/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba][SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541639/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541638/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba][SO_{4}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541640/gif.latex)
![K_{eq} = \frac{[Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]}{[BaSO_{4}(s)]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541651/gif.latex)
![K_{eq}*[BaSO_{4}]=[Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553150/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541654/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag^{2+}][CN^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553641/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag]^{+}[CN]^{-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543653/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag][CN]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543655/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag^{+}][CN^{-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543651/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag][CN^{-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543657/gif.latex)
![K_{eq} = \frac{[Ag^{+}][CN^{-}]}{[AgCN(s)]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543680/gif.latex)
![K_{eq}*[AgCN(s)]=[Ag^{+}][CN^{-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553035/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ag^{+}][CN^{-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/543683/gif.latex)



