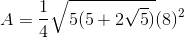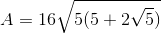All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find An Angle In A Hexagon
Quantitative Comparison
Quantity A: The degree measure of any angle in an equilateral triangle
Quantity B: The degree measure of any angle in a regular hexagon
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity B is greater.
We know the three angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees, and all three angles are 60 degrees in an equilateral triangle.
A hexagon has six sides, and we can use the formula degrees = (# of sides – 2) * 180. Then degrees = (6 – 2) * 180 = 720 degrees. Each angle is 720/6 = 120 degrees.
Quantity B is greater.
Example Question #2 : How To Find An Angle In A Hexagon
Quantity A: Double the measure of a single interior angle of an equilateral triangle.
Quantity B: The measure of a single interior angle of a hexagon.
Quantity B is bigger.
Quantity A is bigger.
The quantities are equal.
The relationship cannot be determined with the information given.
The quantities are equal.
Begin with Quantity A. We know the measure of one angle in an equilateral triangle is 60. Therefore, double the angle is 120 degrees.
For the hexagon, use the formula for the sum of the interior angles:
where n= number of sides in a regular polygon
If the sum of the interior angles of a regular hexagon is 

The two quantities are equal.
Example Question #44 : Plane Geometry
The perimeter of a regular pentagon is 40 units. What is the area of the pentagon?
The formula for the area of a regular pentagon is given by the equation:
where a is represented by the length of one side. Let's begin by finding the side length of the regular pentagon. If the perimeter is 40, then we can divide by 5 (the number of sides) to find a side length of 8.
If we plug in 8 into the equation:
Example Question #1 : How To Find An Angle In A Pentagon
In a five-sided polygon, one angle measures 
To find the sum of the interior angles of any polygon, use the formula 
In this case:
The sum of the interior angles will be 540. Go through each answer choice and see which one adds up to 540 (including the original angle given in the problem).
The only one that does is 120, 115, 95, 105 and the original angle of 105.
Example Question #52 : Plane Geometry
In a particular heptagon (a seven-sided polygon) the sum of four equal interior angles, each equal to 
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined.
Quantity B is greater
Quantity A is greater.
The sum of interior angles in a heptagon is 


Three interior angles (call them 

Further more, all of these angles must sum up to 
We may not be able to find 



Example Question #53 : Geometry

What is the value of 
Always begin working through problems like this by filling in all available information. We know that we can fill in two of the angles, giving us the following figure:

Now, we know that for any polygon, the total number of degrees in the figure can be calculated by the equation:


Thus, for our figure, we have:
Based on this, we know:
Simplifying, we get:
Solving for 

Example Question #53 : Plane Geometry

Quantity A: The measure of the largest angle in the figure above.
Quantity B:
Which of the following is true?
Quantity B is larger.
The relationship cannot be determined.
Quantity A is larger.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is larger.

To begin, recall that the total degrees in any figure can be calculated by:


Now, based on our figure, we can make the equation:
Simplifying, we get:

This means that 

Example Question #1 : Triangles
What is the perimeter of an isosceles triangle given that the sides 5 units long and half of the base measures to 4 units?
The base of the triangle is 4 + 4 = 8 so the total perimeter is 5 + 5 + 8 = 18.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Perimeter Of An Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangle
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side










This Isosceles triangle has two sides with a length of 
To find the missing side, double the value of side 


Therefore, this triangle has two sides with lengths of 

To find the perimeter, apply the formula: 

Example Question #57 : Geometry
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side




To solve this problem apply the formula: 
However, first calculate the length of the missing side by: 
Thus, the solution is:
All GRE Math Resources