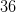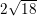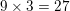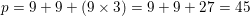All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #12 : Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle ABC is laid flat on its base. Given that <B, located in the lower left corner, is 84 degrees, what is the measurement of the top angle, <A?
Since the triangle is isosceles, and <A is located at the top of the triangle that is on its base, <B and <C are equivalent. Since <B is 84 degrees, <C is also. There are 180 degrees in a triangle so 180 - 84 - 84 = 12 degrees.
Example Question #13 : Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangles
Triangle ABC is isosceles
x and y are positive integers
A
---
x
B
---
y
Quantity A is greater
Quantity B is greater
The two quantities are equal
The relationship cannot be determined
Quantity B is greater
Since we are given expressions for the two congruent angles of the isosceles triangle, we can set the expressions equal to see how x relates to y. We get,
x – 3 = y – 7 --> y = x + 4
Logically, y must be the greater number if it takes x an additional 4 units to reach its value (knowing they are both positive integers).
Example Question #14 : Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle has one obtuse angle that is 
We know that an isosceles triangel has two equal sides and thus two equal angles opposite those equal sides. Because there is one obtuse angle of 112 degrees we automatically know that this angle is the vertex. If you sum any triangle's interior angles, you always get 180 degrees.
180 – 112 = 68 degrees. Thus there are 68 degrees left for the two equal angles. Each angle must therefore measure 34 degrees.

Example Question #1 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles

The obtuse Isosceles triangle shown above has two sides with length 
. The length of side



To solve this problem, apply the formula:
Side 

Since this is an Isosceles triangle, there must be two sides with a length of 
Thus, plug in each side lengths value to find the solution:
Example Question #1 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
The three angles in a triangle measure 3x, 4x + 10, and 8x + 20. What is x?
25
20
30
15
10
10
We know the angles in a triangle must add up to 180, so we can solve for x.
3x + 4x + 10 + 8x + 20 = 180
15x + 30 = 180
15x = 150
x = 10
Example Question #2 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle

In triangle ABC, AB=6, AC=3, and BC=4.
Quantity A Quantity B
angle C the sum of angle A and angle B
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity A is greater
Quantity A and B are equal
Quantity A is greater
The given triangle is obtuse. Thus, angle 





Example Question #3 : How To Find An Angle In An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
In the figure above, what is the value of angle x?
To find the top inner angle, recognize that a straight line contains 180o; thus we can subtract 180 – 115 = 65o. Since we are given the other interior angle of 30 degrees, we can add the two we know: 65 + 30 = 95o.
180 - 95 = 85
Example Question #4 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
What is the area of a triangle with side lengths 18, 24, and 30?
196
280
342
140
216
216
The question doesn't tell us if this is a right triangle, so we can't assume that it is. But there is a formula to find the area when we don't know the height: area = [p(p – a)(p – b)(p – c)]1/2, where a, b, and c are the side lengths and p is half of the perimeter. The perimeter is 18 + 24 + 30 = 72, so p = 72/2 = 36.
Then area = [36(36 – 18)(36 – 24)(36 – 30)]1/2 = [36 * 12 * 6 * 18]1/2 = 216.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of An Acute / Obtuse Triangle
You are asked which triangle is larger. You are only told that theyhave the same base length and that one contains at least one 3 inch side and the other contains at least one 4 inch side. Determine whether the left or right triangle is larger.
It is impossible to determine from the given information.
The triangles are equal
The right triangle is larger
The left triangle is larger
It is impossible to determine from the given information.
Since we are told nothing about the angles we cannot assume that these are isosceles triangles and are open to possibilites such as that shown below in which the left side would be larger. If both were isosceles triangles then the right side would be larger.
Example Question #1 : Acute / Obtuse Triangles
A triangle has sides 3, 5, and x. What can side x not be equal to?
3
6
4
9
9
This question draws from the Third Side Rule of triangles. The length of any side of a triangle must be greater than the difference between the other sides and less than the sum of the other two sides.
This means that side x must be between 2 and 8 since the difference between 5 – 3 = 2 and the sum of 3 + 5 = 8.
Choices 3, 4, and 6 all fall within the range of 2 to 8, but choice 9 does not. The answer is 9.
All GRE Math Resources