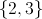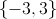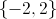All Algebra 1 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2381 : Algebra 1
Solve by completing the square:
no real solution
In order to set this up for completing the square, we need to move the 135 to the other side:
Now the equation is in the form:
To complete the square we need to add to both sides the folowing value:
So we need to add 9 to both sides of the equation:
Now we can factor the left side and simplify the left side:
Now we need to take the square root of both sides:
**NOTE: Don't foget to add the plus or minus symbol. We add this becase there are two values we can square to get 144:

and
**End note
Now we can split into two equations and solve for x:
and
So our solution is:
Example Question #13 : How To Factor An Equation
Factor:
There is a common variable 
Factor 
The common factors that will achieve the middle term and will have a product of 36 is four and nine. Write the binomials.
The cubics here cannot be simplified any further.
The answer is:
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Solution Set
Solve for 
The equation has no solution.
Move one radical to the other side, then square, thereby yielding an equation with only one radical.
Isolate the radical on one side, then square.
Substitution confirms this to be the only solution.
Example Question #2 : How To Find A Solution Set
If the area of a rectangle is 100 square feet and the width is 20 feet, then what is the perimeter?
80 feet
30 feet
20 feet
50 feet
50 feet
The area of a rectangle is 





Example Question #3 : How To Find A Solution Set
Solve for 
The equation has no solution.
Cube both sides of the equation to form a linear equation, then solve:
Example Question #1 : Solving Equations
Solve this system of equations.












Equation 1:
Equation 2:
Equation 3:
Adding the terms of the first and second equations together will yield 
Then, add that to the third equation so that the y and z terms are eliminated. You will get 
This tells us that x = 1. Plug this x = 1 back into the systems of equations.
Now, we can do the rest of the problem by using the substitution method. We'll take the third equation and use it to solve for y.
Plug this y-equation into the first equation (or second equation; it doesn't matter) to solve for z.
We can use this z value to find y
So the solution set is x = 1, y = 2, and z = –5/3.
Example Question #2 : Solving Equations
Solve for 
To solve this problem we can first add 
Then we take the square root of both sides to get
Then we calculate the square root of 

Example Question #121 : Functions And Graphs
Determine where the graphs of the following equations will intersect.
We can solve the system of equations using the substitution method.
Solve for 
Substitute this value of 
Now we can solve for 
Solve for 

The solution is the ordered pair 
Example Question #1 : Solving Equations And Inequallities
Give all real solutions of the following equation:
By substituting 

We are looking to factor the quadratic expression as 


Substitute back:
The first factor cannot be factored further. The second factor, however, can itself be factored as the difference of squares:
Set each factor to zero and solve:

Since no real number squared is equal to a negative number, no real solution presents itself here.
The solution set is 
Example Question #3 : How To Find A Solution Set
Solve for 
Subtract 12 from both sides:
–3x = –15
Divide both sides by –3:
x = 5
All Algebra 1 Resources













































![\sqrt[3]{2n-8} = -4](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/96246/gif.latex)




![\sqrt[3]{2n-8} = -4](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/123718/gif.latex)
![\dpi{150} \left (\sqrt[3]{2n-8} \right ) ^{3}= \left (-4 \right )^{3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/96247/gif.latex)